* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earthquake Notes
Ionospheric dynamo region wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
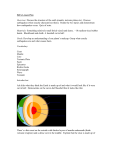
Earthquakes Earthquakes occur when vast plates, or rocks, within the Earth suddenly break or shift under stress, sending shock waves rippling. Sudden movement along the fault causes the ground to shake. Most earthquakes occur along fractures in the Earth's crust called faults. Intraplate quakes occur far from plate edges and happen when stress builds up and the Earth's crust is stretched or squeezed together until it rips. There are several different types of faults. Each can be a few inches or many hundreds of miles long. They can be horizontal, vertical, or at an angle. Earthquake waves are measured on sensitive instruments called seismographs. The Richter scale assigns quakes a number based on the power of its seismic waves. Thousands of quakes occur every day around the globe, most of them too weak to be felt. Every year about 10,000 people, on average, die as a result of earthquakes