* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Growing and Flowing Study Guide answer key
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
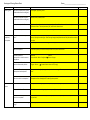
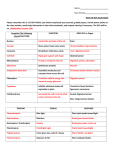
Growing and Flowing Review Sheet Topic Flowering Parts Photosynthesis/ Respiration/ Transpiration Biotic and Abiotic Factors Name __________________________________ Question What are the female parts of a plant? (Be able to label them on a diagram) Answer Pistil, Stigma, Style, Ovary, Ovule Page in the ISN What are the male parts of a plant? (Be able to label them on a diagram) Stamen, Anther, Filament, Pollen How do plants reproduce? Pollen is transferred from the anther to the stigma by a pollinator. The pollen travels down the style and fertilizes the ovules. The ovary becomes a fruit, and the ovules become seeds. How does a flower protect itself? The sepals and the petals surround the reproductive organs so that the flower is able to reproduce. What is photosynthesis? Why does it occur? Process by which plants make food. Sunlight combines with chlorophyll and abiotic factors (carbon dioxide and water) to form glucose and oxygen. Plants must go through photosynthesis because they are unable to consume their food. What is respiration? Process organisms use to release the energy stored in the glucose. What is transpiration? Evaporation of water from leaves that helps to balance the plant’s water content Write the equation for photosynthesis. Label the reactants and products. Reactants Carbon dioxide + Water + Sunlight Write the equation for respiration. Label the reactants and products. Reactants Oxygen + Glucose What is the difference between photosynthesis and respiration? Photosynthesis makes (food) energy and respiration releases energy. These two processes are opposites of each other. What is the role of the stomata? What is the role of the chloroplasts? Stomata are tiny holes that exchange gases and allow water to evaporate. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll that is needed for photosynthesis. What are biotic factors? Biotic factors are the living things in an ecosystem. (Plants, animals, organisms) What are abiotic factors? Abiotic factors are the nonliving things in an ecosystem. (Air, water, soil) How do abiotic factors affect biotic factors in an ecosystem? Abiotic factors combined with biotic factors allow for processes such as photosynthesis and respiration and start the food chain What are the basic needs for all living things? Air, water, food, shelter Products Glucose + Oxygen Products Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATP (Energy) Growing and Flowing Review Sheet Food Chains/ Food Webs Plant Adaptations Name __________________________________ How do these factors work together in an ecosystem? Ecosystems are codependent systems. Everything within an ecosystem needs other factors in order to thrive and survive. For example, consumers need producers, producers need sunlight, etc. How does energy flow within an ecosystem? Energy is created in the plants (producers). Consumers take in the producers and the energy is then transferred to the consumer. Food chains and energy pyramids show how energy is transferred. What is a food chain? See vocabulary What is a food web? See vocabulary Why does energy decrease as you move toward the top of the energy pyramid? Less energy is available as more energy is needed by the higher organisms. What is a producer? Give two examples. Definition: See vocabulary Examples: grass, trees What is a consumer? Give two examples. Definition: See vocabulary Examples: humans, lions, cows What is a decomposer? Give two examples. Definition: See vocabulary Examples: mushrooms, fungi What are plant adaptations? Give three examples. Definition: Plant adaptations are changes that a plant makes in order to survive in its environment Examples: Answers will vary (tropisms, longer roots) What is phototropism? Draw a picture that shows phototropism. Definition: A plant’s response to light. Can be either positive (toward the light) or negative (away from the light) Picture: What is gravitropism? Draw a picture that shows gravitropism. Definition: A plant’s response to gravity. Can be either positive or negative Picture: What is thigmotropism? Draw a picture that shows thigmotropism. Definition: A plant’s response to touch. Can be either positive or negative. Picture: How can tropisms help a plant survive? The response to stimuli can save the plant or help pollinate, climbing helps get to light, which plants need for photosynthesis.