* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transition Metal Complexes
Bond valence method wikipedia , lookup
Oxidation state wikipedia , lookup
Jahn–Teller effect wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Metal carbonyl wikipedia , lookup
Cluster chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Spin crossover wikipedia , lookup
Stability constants of complexes wikipedia , lookup
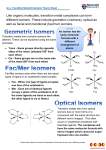
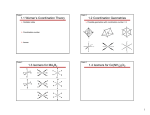
Transition Metal Complexes - Structure Coordination Sphere Outer-sphere Inner-sphere What Is A Coordination Compound? http://www.chem.purdue.edu/gchelp/cchem/ Low Coordination Four Coordination Common for: 1st Row metal with donor ligands Four Coordination Four Coordination Common for: 1st Row d8 with acceptor ligands 2nd & 3rd Row d8 Four Coordination Geometric Isomerism Five Coordination Five Coordination Five Coordination Berry pseudorotation Six Coordination Oh Six Coordination D4h D2h D4h D3d Six Coordination Seven Coordination Eight and Higher Coordination Polymetallic Complexes Nomenclature Rules 1. The ligands are named first; the prefixes di, tri, tetra, and so on are used to indicate the number of each kind of ligand present. [Sometimes the prefixes bis (2 ligands), tris (3 ligands), and tetrakis (4 ligands) are also used, especially when the ligand name is complicated or already includes di, etc.] Negative ligands are given names which end in -o. Nomenclature Rules 2. The ligand names are given in alphabetical order. Some ligands have familiar names also used in naming other types of compounds (eg. chloro, cyano); others have names special to complexes (eg. carbonato, CO32-; aqua, H2O). 3. The name of the central metal atom or ion followed by its oxidation state in parentheses is given after the ligand names (not separated by a space). Nomenclature Rules 4. When a complex ion has a negative charge, the name of the central metal atom is given the ending ate. For some of the elements, the ion name is based on the Latin, for example, ferrate for iron, Fe; plumbate for lead, Pb. When naming only the ion, the word "ion" is always used in the name. In naming a co-ordination compound, the name of the cation is given first as usual, followed by the name of the anion. Examples K+[Pt(NH3)Cl5]potassium amminepentachloroplatinate(IV) [Co(NH3)4SO4]+ NO3tetraamminesulfatocobalt(III) nitrate Examples Re2Cl82Octachlorodirhenate(III) (H3N)5CrOCr(NH3)54+ -oxobis[pentaamminechromium(III)] Ligand Nomenclature Ligand FClBrICNSCNNCSNO2ONOOH- Name fluoro chloro bromo iodo cyano thiocyanato isothiocyanato nitro nitrito hydroxo Ligand Name O2oxo OSO32- sulfato (SO42-) OSO22- sulfito (SO32-) CO32- carbonato C2O42- oxalato NH3 ammi ne( not i ce2m’ s) H2O aqua CO carbonyl NO nitrosyl PR3 trialkyl- or triarylphosphine SCN- - ambidentate ligand Polydentate Ligands and Chelate Some Bidentate Ligands Ethylenediammine (en) Acetylacetonate ion (acac) Phenanthroline (phen) Oxalate ion (ox) Polydentate Ligands and Chelate Polydentate ligand –ligand with more than one site to connect to a metal center Monodentate, bidentate, tridentate, …… Chelate –polydentate ligand/metal ring Bite Angle •Small bite angle may distort the geometry from ideal structure Isomerism Structural isomers: contain the same number and kinds of atoms, but one or more bonds is/are different (i.e., the connectivity between atoms is different). There are two types of structural isomers: coordination isomers, and linkage isomers Stereo isomers: contain the same number and kinds of atoms, and the same number and kinds of bonds (i.e., the connectivity between atoms is the same), but the atoms are arranged differently in space. There are two types of stereo isomers: geometric isomers, and optical isomers Linkage Isomerism [Fe]-SCN [Fe]-NCS Geometric Isomerism Geometric Isomerism facial fac meridional cis trans Optical Isomerism Chiral –enantiomer pair achiral Optical Isomerism right hand screw left hand screw