* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Honors Physics Chapter 21electromagnetic induction
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
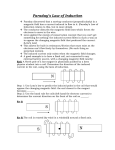
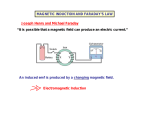
Warm-up • Why do loops of wire in a motor rotate? • What is similar between Electric motor, and Electric meter? • What is electromagnetic induction? • Name 4 objects that apply electromagnetic induction. Chapter 37: Electromagnetic Induction • 1. Faraday discovered: Magnetic and Electric fields interact to produce a Force. (3rd right hand rule) 2. Magnetism can produce electric current in a wire!! • How so? • Michael Faraday Electromagnetic Induction • The phenomenon of inducing voltage in a conductor by changing the magnetic field near a conductor is known as Electromagnetic Induction Magnetic field changes when either the magnet or the coil moves or when they both move. Faradays experiment • Molecular Expressions: Electricity and Magnetism - Interactive Java Tutorials: Faraday's Magnetic Field Induction Experiment Electromagnetic induction • video • http://glencoe.com/sec/science/phys ics/ppp_09/animation/Chapter%202 5/Electromagnetic%20Induction.swf Induced Emf (Voltage)? • why is the phrase Induced voltage used instead of induced current? • Answer: – In order for current to flow between two points of a conductor, there must be a difference of potential between those points. That potential difference is the voltage. Therefore, Voltage (Emf) is induced first in order for current to flow. Application of electromagnetism • Generator • The coil is rotated mechanically using one’s hand, • Other ways of rotating the coil include – Water-hydro power – Wind- wind mills – Steam• Geothermal, • Nuclear Reactors Lenz’s Law Question; • Why is it hard to move the magnet into the coil if the coil has many loops? Lenz’s Law • The law notes that; – an induced voltage always produces a magnetic field that opposes the field that originally produced it. Lenz’s law Magnitude of the induced Emf () • • What factors affect the magnitude of the induced Emf () /voltage? Answer: 1. The rate at which magnetic flux is changing, 2. The number of coils/turns (N) of the conductor Magnetic flux • Magnetic flux is the product of the average magnetic field (B) and the perpendicular area that it penetrates. • If the magnetic field penetrates the area at an angle, magnetic flux is determined using the formula: B B A cos Example • A square loop of wire 10.0 cm on a side is in a 1.25 T magnetic field at an angle of 350. Calculate the flux through the loop. B B A cos Homework • Textbook pg 609 # 1-8 The Faradays law. • Induced Emf () or (Voltage) in a coil is proportional to the product of; – the rate at which the magnetic flux changes within the loops, and – Number (N) of loops (turns /coils) B N t The negative sign indicates the direction of induced emf. The direction of induced current is such that its magnetic field opposes the original change in flux Example; • A square coil of length 5 cm contains 100 loops and is positioned perpendicular to a uniform 0.6 T magnetic field. If the coil has a resistance of 100Ω and is pulled across the field in 0.1 seconds, calculate a) The rate of change of flux b) Induced emf and induced current Applying Lenz’s law • Increasing the external magnetic field. – The conductor gets induced with current whose magnetic field is in the opposite direction to that of the external field. S Magnet with its North Pole facing the coil is moved towards the coil (increasing B) What is the direction of induced current? (use 1st Right hand rule) Applying Lenz’s law • Decreasing the external magnetic field. – The conductor gets induced with current whose magnetic field is in the same direction as that of the external field. N Magnet with its South Pole facing the coil is moved away from the coil (decreasing B) What is the direction of induced current? Exercise B, page 589 I decreasing I increasing I constant I increasing What is the direction of the induced current in the circular loop due to the current shown in each part of this figure? Emf induced in a moving Conductor • When a conductor of length l moves through a magnetic field B at a velocity v, Induced emf is given by the formula; Bl v If the angle between the direction of conductor’s velocity and the magnetic field is changing from being perpendicular to any other angle, The induced Emf on the conductor at that angle becomes; B l v sin Example • An air plane travels at 1000km/h speed in a region where the earth’s magnetic field of 5.0 x 10-5 T is perpendicular to the plane. What is the induced Emf on the planes wings of width 70 m? Class work • Textbook page 610 # 1-10 Generator Equation • For an rectangular coil with two side lengths rotating within a magnetic field like in a Generator, the induced emf is given by; 2B l v sin The transformers A simple transformer • A simple transformer is a set of induction coils as shown below. Primary coil induces voltage onto the secondary coil Primary and secondary coils • A common transformer is made up of an iron core and two coils of wires as shown below. • The Primary coil is connected to the power source. • The secondary coil gets induced with current. What does it do? • Molecular Expressions: Electricity and Magnetism - Interactive Java Tutorials: Transformer Induction process (Mutual induction) • Happens when current in the primary is changing (increasing or decreasing). • Changing current induces a magnetic field that is changing continuously on the core, a condition necessary for induction of voltage continuously on to the secondary coil. • When current is not changing (increasing or decreasing), there is no induction taking place. Why is the AC preferred to DC? • We can increase and decrease current flow by opening and closing (Switching off and on) the circuit continuously when using a DC current, or just use AC current. The Ac is changing continuously Why is an Iron core preferred to two coils apart? • Answer: Iron core concentrates the magnetic field within itself by forming loops that get into contact with the secondary coil. These loops of magnetic field induce voltage in the secondary coil. Step up Transformers • The number of coils in the secondary and primary determines whether a transformer is a step up or step down transformer. less number of coils in primary more number of coils in secondary Step down Transformers Notice that power transferred is the same. More number of turns in primary coil Less number of turns in secondary • What is the relationship between primary voltage, secondary voltage and the number of turns? • Answer: Vp Vs Np Ns • The relationship between in-put and out-put power is: Power input = power output. I p V p = Is Vs Class work & Homework • Textbook Page 612, # 30-36