* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exploration and Expansion
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
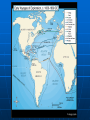
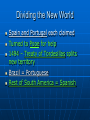
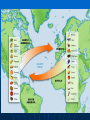
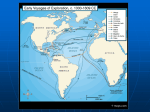
Exploration and Expansion Essential Questions What factors contributed to the Europeans entrance into their age of discovery and expansion? What were the general consequences of European expansion? Technology Compass (China) Astrolabe (Arabs) Cartography (Ptolemy & Byzantine & Arabs) – latitude and longitude Triangle-shaped sails (Arabs) Gunpowder (China) Multiple masts Reasons for Expansion Trade with Asia • Marco Polo • Spices • Cut off by Arab empires Economic and political expansion Three G’s • Gold - Wealth • Glory – Power/Empire • God - Christianity Traveled down coast of Africa (Gold Coast) and over to India (spices) Prince Henry the Navigator – 1419, established a school for sailors Bartholomew Diaz – 1487, Cape of Good Hope Vasco da Gama – 1498, around Africa to India Portuguese Spanish Columbus (1492) • • • • • Convinced Queen Isabella to support his journey Landed on San Salvador, Hispaniola, and Cuba Called natives “Indians” Never realized he wasn’t in Asia Amerigo Vespucci – suggested Columbus found the “New World” (Amerigo = America) Magellan • • • • • 1519 Portuguese sailor sailing for Spain Sailed around S. America (Straight of Magellan) Named and crossed the Pacific Ocean Killed in the Philippines Del Cano led ship that circumnavigated the world Dividing the New World Spain and Portugal each claimed Turned to Pope for help 1494 – Treaty of Tordesillas splits new territory Brazil = Portuguese Rest of South America = Spanish Spanish Empire Columbian Exchange • Europe Received – corn, cocoa, potatoes, sweet potatoes, beans • Americas Received – horses, cows, pigs, sugar; ultimately disease (small pox) Conquistadors • Cortes – took over Aztecs in Mexico • Pizarro – took over Incas in Peru Encomienda • Indians became slaves controlled by Spanish • Indians were converted to Catholicism • Bartolome de las Casas –monk; helped Indians European Rivals Dutch (Netherlands) • Trading company in India • Henry Hudson (1621) – claimed New Amsterdam on the Hudson River French • Looked for the Northwest Passage through America • Da Verrazano, Cartier (Montreal), Champlain (Quebec) • Fur trade w/Indians English • John Cabot • Francis Drake - first Englishman to circumnavigate; raided Spanish ships • Jamestown – John Smith – 1st perm. Engl. Settlement (1607) English New England settled by Pilgrims (Plymouth) and Puritans (Mass. Bay) Religious freedom Felt Anglican Church needed reforms Pilgrims – Mayflower Mayflower Compact – selfgovernment; important document in US History New Economic Systems Joint Stock Companies (like corporations, investments) invested in colonies for profit Rise of Capitalism – means of production are privately owned; supply and demand Mercantalism – mother country benefits from colonies by exporting more than they import; gain large amounts of gold/wealth Triangular Trade – Europe, Africa, Americas; key product: slaves Slave Trade Slavery not new to Africa • Sent to Middle East for domestic work Sugarcane (Portuguese) • Changed slavery for Europeans • Plantations in Caribbean and Brazil Grew fast • 16th century – about 275,000 • 17th century – over 1 million • 18th century – over 6 million African slave traders controlled slave trade Middle Passage Destroyed traditional African societies as demand for slaves increased Middle Passage Results of Expansion In Europe • Economically successful • Created rivalries as countries fought over colonies In Asia • Increased trade with Europe • Beginning of “Western dominance” In Africa • Dramatic increase of slave trade • European influence in the coastal areas In the Americas • Destroyed native population • Began European dominance (Spanish)