* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exploration and Expansion
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
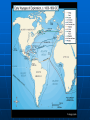
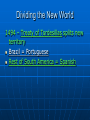
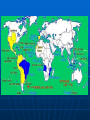
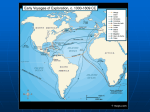
Exploration and Expansion Essential Questions What factors contributed to the Europeans entrance into their age of discovery and expansion? What were the general consequences of European expansion? Technology Compass (China) Astrolabe (Arabs) – latitude/longitude Triangle-shaped sails (Arabs) - faster Reasons for Expansion Three G’s • Gold (Economic) – Wealth; markets in Asia (spices) • Glory (Political)– Power Strong monarchies (Portugal, Spain, France, England) Humanism/Renaissance • God – (Religious) Christianity Prince Henry the Navigator – established a school for sailors Bartholomew Diaz – 1487, Cape of Good Hope in S. Africa Vasco da Gama – 1498, around Africa to India Portuguese Spanish Columbus (October 12,1492) • • • • • Ferdinand and Isabella – Spain Need a western route to Asia – why? San Salvador (Bahamas) Called natives “Indians” Made 3 more trips; never knew he had discovered a new continent Magellan • Circumnavigated the globe – first complete western water route to Asia • He died in the Philippines Dividing the New World 1494 – Treaty of Tordesillas splits new territory Brazil = Portuguese Rest of South America = Spanish Spanish Empire Columbian Exchange • Europe Received – corn, cocoa, potatoes, sweet potatoes, beans • Americas Received – horses, cows, pigs, sugar; ultimately disease Conquistadors • Cortes – conquered Aztecs in Mexico • Pizarro – conquered Incas in Peru European Rivals Dutch (Netherlands) • New Netherlands (NY) • Dutch East India Company French • Looked for the Northwest Passage through America • Champlain (Quebec) • Fur trade w/Indians English • 1607 -Jamestown – John Smith – 1st perm. English settlement • Oldest settlement? (1565) Slave Trade Slavery not new to Africa • Sent to Middle East for domestic work Sugarcane (Portuguese) • Changed slavery for Europeans • Plantations in Caribbean and Brazil African slave traders controlled slave trade Middle Passage Destroyed traditional African societies as demand for slaves increased Middle Passage Results of Expansion Great wealth for European nations – greed and power Rivalries developed over colonies Increased European trade with Asia Colonization of the Americas Destruction of Native populations (disease, superior technology) Dramatic increase in the slave trade African civilizations destroyed New products (Columbian Exchange)