* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Life Cycle of a Plant
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
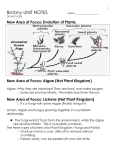
The Life Cycle of a Plant Today’s Learning Goal • Earlier this week, you planted a Wisconsin Fast Plant! Now you are eagerly waiting to observe its life cycle. • To help you build background on the stages of a plant’s growth, you will read some slides today, take notes from them on the stages of a plant’s growth, draw some diagrams, and possibly view some plant videos. Your instructions • Make a heading in your notebook for The Life Cycle of a Plant. • Read each slide carefully. • For each slide, write down • The heading (like 1. Germination) • Copy the information down for that part of the life cycle. • When you are done with writing the notes, follow the directions on the other slides. The Life Cycle of a Plant 1. Germination • The seed coat is softened by water. • The seed splits open. • The new plant inside (the embryo) begins to grow up. • The root begins to grow down into the soil. 2. Sprout or Seedling • A small shoot pushes up through the soil, beginning the plant’s growth. • The stem and “seed leaves” turn green as CHLOROPHYLL (a green chemical) begins to form. Chlorophyll is one the things needed for a plant to make its own food. 3. Plant Growth • The stem grows thicker and stronger. • The plant becomes green with CHLOROPHYLL inside it. • It develops LEAVES, which are “food factories”. They make food for the plant by the process of PHOTOSYNTHESIS. • The plant grows taller. 4. Flower buds • Flower buds begin to form at the tips of some stems. • They are important beginnings of new flowers, from which new seeds will form. 5. Flowers • A flower opens its colorful petals up, with important parts in the center to help to create a new seed. 6. Pollination • An insect, bird or the wind has to help transfer pollen grains from the plant of one flower to a flower of a different plant. • The flower is then fertilized and a new seed begins to grow inside the flower. 7. Fruit or seed pod formation • A fruit or seed pod grows around the seed to protect the seed. • The flower dies and the fruit or seed pod dries up and splits open, releasing the seeds. 8. Seed dispersal • The seeds fall out of the fruit or seed pod into the soil, or gets carried to a new location by the wind, water or animals. • Some seeds have hooks, burrs, or sticky surfaces to help them travel. • Once they fall on new soil, the life cycle begins again, as the seed goes into the ground and germinates. Life Cycle in Pictures • You will draw a series of diagrams/pictures in your notebook to show the life cycle of a plant in pictures. • Press “Escape” to get out of full-screen view of the presentation. • Scroll back to 1. Germination. • Write the heading for the slide, and draw a diagram based on one of the illustrations on the slide. Do your best to draw it accurately! Add color if you can! If you are done…. • Go to www.kyrene.org • Click Students, then Educational Resources, then choose Discovery Education. • Log in with your usual Kyrene number and password. • Once you are in, type “Plants” in the Search box at the top. Put on headphones and watch some video clips about plants!