* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Applied Biology Chapter 8 Study Guide
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
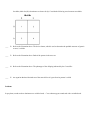
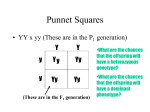
Applied Biology Chapter 8 Study Guide ____ 1. The “father” of genetics was ____ 2. What is the probability that the offspring of a homozygous dominant individual and a homozygous recessive individual will exhibit the dominant phenotype? ____ 3. The first filial (F1) generation is the result of ____ 4. The passing of traits from parents to offspring is called ____ 5. The phenotype of an organism ____ 6. If an individual has two recessive alleles for the same trait, the individual is said to be ____ 7. An individual heterozygous for a trait and an individual homozygous recessive for the trait are crossed and produce many offspring. These offspring are likely to be ____ 8. Tallness (T) is dominant over shortness (t) in pea plants. Which of the following represents the genotype of a pea plant that is heterozygous for tallness? ____ 11. How many different phenotypes can be produced by a pair of codominant alleles? In rabbits, black fur (B) is dominant over brown fur (b). Consider the following cross between two rabbits. ____ 12. Refer to the illustration above. The device shown, which is used to determine the probable outcome of genetic crosses, is called a ____ 13. Refer to the illustration above. Both of the parents in the cross are ____ 14. Refer to the illustration above. The phenotype of the offspring indicated by box 3 would be ____ 15. An organism that has inherited two of the same alleles of a gene from its parents is called Problems In pea plants, round seeds are dominant over wrinkled seeds. Cross a heterozygous round seed with a wrinkled seed. Blood types are an example of codominance. Cross a person with heterozygous A blood with a person with type O blood. Incomplete dominance problem: Red and white 4 o’clock flowers are an example of incomplete dominance. Cross two red flowers. Vocabulary - Will be a matching section on the test A) B) C) D) E) F) G) heredity incomplete dominance homozygous lowercase allele hybrid capital H) I) J) K) L) M) Gg phenotype codominance purebred color-blindness heterozygous