* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart Conditions - Children`s Health Center
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
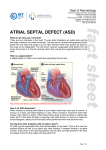
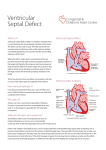
Cardiac Disorders in Children Atrial Septal Defect An atrial septal defect (ASD), typically called a "hole in the heart," is a congenital heart defect in which the wall between the two chambers of the atria, the septum, has an opening in it. This allows oxygenated blood from the left atrium into the right atrium, where it mixes with the blood that is not oxygenated and increases the blood flow to the lungs. This creates a heart murmur. According to KidsHealth.org, ASD can be genetic, but many cases have no single identifiable cause. Treatment depends on where the hole is in the septum and how big it is. Very small defects can heal on their own, but most children with this condition require surgery with either catheterization or openheart surgery if the hole has not closed by the time they start school. Tetralogy of Fallot Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is actually four different heart conditions that occur concurrently, according to Cincinnati Children's Hospital. These four conditions are pulmonary stenosis, or the narrowing of the pulmonary valve and the area below the valve, causing blockage between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery; ventricular septal defect, which is a hole between the two chambers of the heart; an overriding aorta, which means the aortic valve is enlarged; and right ventricular hypertrophy, which is a thickening of the walls of the right ventricle. Symptoms can include heart murmur, a bluish appearance due to lack of oxygenated blood and rapid breathing. Depending on the oxygen level in the blood, treatment consists of one or more surgeries, typically around 6 months of age. Coarctation of the Aorta Coarctation of the aorta (COA) is a narrowing of the aorta, the main blood vessel that enables blood to flow from the heart to the rest of the body. This narrowing may occur anywhere along the aorta. When this happens, the left side of the heart needs to work even harder in order to ensure that blood flows through the aorta, even though it is narrowed. The narrowing can be very minor and not even noticeable or it can be a major constriction that impacts the left ventricle of the heart. KidsHealth.org estimates that COA makes up approximately 8 percent of congenital heart problems. Diagnosis typically occurs when the child is young, but in minor cases, the defect may not be diagnosed until adolescence. Symptoms may include cold legs and feet, chest pain and trouble catching the breath, particularly during exercise. Through an electrocardiogram, chest x-ray, MRI or CT scan, an accurate picture of the heart can be obtained. Severe COAs are typically treated with surgery soon after birth. In other cases, a balloon angioplasty may be done, a stent may be placed in the heart, or the narrowed part of the aorta may be removed and the two ends joined Kawasaki Disease Kawasaki disease, also called Kawasaki syndrome or mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome, is one of the main causes of acquired heart disease in children in the United States, according to the American Heart Association (AHA). The large majority of children with this disease are diagnosed by the time they are 5 years old, and it is rarely diagnosed in children over 8 years of age. Symptoms include swollen hands and feet, rash, irritation and redness in the whites of the eyes, swollen lymph nodes and inflammation in the mouth and throat. Although a definitive cause is not known, it is hypothesized that a virus causes this disease. The AHA estimates that 15 to 25 percent of children who have Kawasaki disease have heart damage; in most cases, the coronary arteries are weakened. The heart may also be inflamed, as well as the sac surrounding the heart, and abnormal heart rhythms called arrhythmias may occur. These heart problems typically resolve in five to six weeks but can be life-long in some individuals. Treatment can include aspirin to reduce fever and inflammation, and intravenous gamma globulin can be given early in the disease to help reduce the risk of coronary artery damage. Infant Heart Problems Cause: The fetal heart forms between the sixth and 12th week of development, which is often before a woman realizes that she is pregnant. While a majority of heart defects have no identifiable cause, exposure and infection to certain bacteria, viruses and parasites during early pregnancy will put the fetus at risk for abnormal heart development. Group B Strep, Chickenpox, certain vaccinations, Listeria---a bacteria found in contaminated food, toxoplasmosis---caused by a parasite, cytomegalovirus---a common virus, can all cause infant heart problems. The CDC also says poorly controlled diabetes in the mother also increases the risk of infant heart abnormalities Types Types of infant heart problems include hypoplastic left heart syndrome, which relates to several infant heart problems that cause an underdeveloped left heart structure. This condition results in decreased oxygen-rich blood flow to the body, says the CDC. Another condition is a ventricular septal defect, which is a hole in the partition separating the ventricles, the main pumping chambers of the heart. An atrial septal defect is a perforation or hole in the partition separating the two atria, or upper chambers of the heart. Transposition of the great arteries occurs when the pulmonary artery and the aorta arise from the wrong sides of the heart. Symptoms Many of these infant heart problems involve too much blood in the lungs and not enough blood in the body, leading to difficulty breathing and severe fatigue. These symptoms often indicate an oxygen deficiency, which compromises how the cells generate energy. Symptoms also include difficulty feeding, which can lead to poor nutrition and development. Complications A serious heart condition can be life threatening if not corrected. A less severe problem can cause stunted growth and underdeveloped muscles and limbs. Repeated infections due to complications and impaired circulation can cause permanent lung and organ damage. The infant will also tire easily and not gain weight appropriately. According to the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, more than 35,000 babies are born annually in the United States with congenital heart defects with varying levels of severity. Diagnosis Ultrasound will often uncover these infant heart problems before birth. This approach is useful because it allows doctors to prepare for emergency treatment at birth, before the condition can cause permanent damage to other organs. In some cases, these heart problems will not become evident until after the baby is born. Tests such as arterial blood gases, electrocardiography, echocardiography and cardiac catherization will confirm the diagnosis and level of severity. Treatment Minor heart conditions such as small septal defects may become less severe and resolve on their own as the infant grows, says the CDC. Medication and supplemental oxygen will support circulation and lung function, sometimes improving the infants' condition and eliminating the need for surgery. Other defects are likely to worsen and require immediate surgical intervention. In severe cases, a heart transplant is the only option.