* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pedigree Exercise
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Tay–Sachs disease wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome-wide association study wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
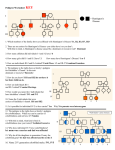
Bio CP – Mendelian Genetics How to make a Pedigree Chart? Genetic counseling provides information and counseling to couples who wish to have children but are worried that they might pass a disease to their children. Genetic counselors often make use of a diagram known as a pedigree, which is a tool for tracing a trait through generations of a family. By making a pedigree, it is often possible to predict whether a person is a carrier of a heredity disease. When you look at the chart note that: Females are circles, males are squares. Completely filled in circles or squares are affected, which means they have the trait you are mapping. Half-filled in circles or squares are carriers, which mean that they have one copy of the allele, but not the trait. To be a carrier, the trait must be recessive! Each Generation gets its own line with the oldest at the top. Notice that siblings are connected with a line above their shape. Spouses are connected with a line in the middle of their shape. Bio CP – Mendelian Genetics Pedigree 1 Autosomal Dominant: The following is the pedigree of a disease that is controlled by a dominant allele. It is NOT X-linked 1. Can there be carriers for a disease that is controlled by a dominant allele? 2. How many generations are shown in the pedigree? 3. How many individuals have at least one allele for this disease? Pedigree 2: Tracing the path of an autosomal recessive trait Trait: Falconi anemia Forms of the trait: The dominant form is normal bone marrow function - in other words, no anemia. The recessive form is Falconi anemia. Individuals affected show slow growth, heart defects, possible bone marrow failure and a high rate of leukemia. A typical pedigree for a family that carries Falconi anemia. Note that carriers are not indicated with halfcolored shapes in this chart. Analysis Questions. To answer questions #1-5, use the letter "f" to indicate the recessive Falconi anemia allele, and the letter "F" for the normal allele. 1. What is Arlene's genotype? 2. What is George's genotype? 3. What are Ann & Michael's genotypes? 4. Most likely, Sandra's genotype is . Bio CP – Mendelian Genetics Pedigree 3 : X-linked recessive 1. For each family member, write the genes and alleles he or she has inherited for color vision below the circle or square on the pedigree. Remember color vision is an X-linked trait. Use these symbols: o XC represents a dominant allele for normal color vision o Xc represents a recessive allele for color blindness o Y represents the chromosome passed from father to son. It does NOT contain any allele for seeing color. 2. One of the two brothers with normal color vision in the third generation of this pedigree (lower right) has a colorblind son and two daughters with normal vision, but who are carriers. What must the genotype of his wife be? Draw the punnett square to support your answer. 3. Using the correct symbols, add this marriage and the children to the pedigree. Bio CP – Mendelian Genetics Pedigree 4: Shown below is a pedigree chart for the inheritance of achondroplasia, or dwarfism. Dark circles or squares indicate individuals with achondroplasia. a. How many females are there in the second generation? b. Are any carriers shown on this pedigree? c. Is the gene that causes this form of dwarfism a recessive or dominant trait? How do you know? Hint: look at the family on the lower right. d. Draw the punnet square for the family on the lower right. Bio CP – Mendelian Genetics Draw a pedigree for the following family to trace BLUE EYES (so blue eyed people are shaded). You will need to think about the genetics in a few places to determine if people are homozygous or heterozygous. Jan and Bob both have brown eyes. They have two kids: a boy and a girl who both have blue eyes. Jan’s mom has blue eyes and her dad has brown eyes. Bob’s mom has blue eyes and his dad has brown eyes. Bob has 1 sister with blue eyes. Jan has 4 siblings: 1 brother with blue eyes, 1 sister with blue eyes and two sisters with brown eyes. If Jan’s blue eyed sister married a blue eyed man, could they have brown eyed children? Explain. Also show your punnett square.