* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 8 * Section 3
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
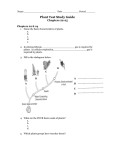
Chapter 8 – Section 3 The Characteristics of Seed Plants What are Seed Plants? • Seed plants outnumber seedless plants 10 to 1 • Have vascular tissue • Use pollen and seeds to reproduce Vascular Tissue • Meets the Challenges – stand up straight, supply all cells with food and water. • Phloem – food moves through this tissue • Xylem – water and minerals travel through this tissue Pollen and Seeds • Do not have to live in water as don’t have sperm that has to swim • Pollen-tiny structures that contain the cells that later become the sperm • Seeds are made when the sperm fertilizes the egg. – Young plant inside a protective covering, Right conditions sprout breaks out of seed. Seed Structure – Figure 10 p. 264 3 parts Embryo – plant that develops from zygote Seed food – some stored in cotyledons (seed leaves in embryo) or outside the embryo Seed coat – outer covering (protects from drying out) Seed Dispersal- scattering of seeds • Other organisms waste • Barbs that hook on other animals • Wind • Eject from plant with force Seed Germination- when embryo begins to grow again and pushes out of seed • Begins when seed absorbs water and begin to grow • Roots grow first downward, stem and leaves upward • Seedling- when you see the leaves • Distance from parent needed Roots • 3 Main functions • Anchor a plant to ground • Absorb water and minerals from the soil • Sometimes store food Types of Roots- Figure 13 p 267 1. Fibrous Root Systemseveral root systems that form a dense tangled mass- grass 2. Taproot Root System – One long thick root smaller branching off. dandelion Structure of Root-figure 13 p. 267 • Tip round, covered by root cap (protects from injury from rocks as it grows) • Root hairs absorb the water and minerals, help anchor plant • Vascular tissue –water moves to xylem and upward • Phloem – transports food from leaves to roots Stems – • carries substances between roots and leaves • supports • holds up leaves to get sun Stem structure- figure p. 268 • Herbaceous – no wood • Woody • hard, rigid • several layers, • outer layer bark • Cambium – cells that divide to procduce phloem and xylem (wood part) • All have phloem and xylem Annual Rings • Made up of xylem • Summer grow slow and make small rings • Spring grow fast and make dark large rings Leaves • Capture suns energy and carry out the food making process of photosynthesis • Come in many different shapes Structure of Leaf- figure 16 p. 270 • Surface layers – Protect cells – Veins that contain xylem and phloem – Have stomata (pores that open and close to control gases going in and out) • CO2 in and H2O and Oxygen out. Leaf and Photosynthesis • Upper surface has most cells with chloroplasts (chlorophyll in the chloroplasts trap sun’s energy) • CO2 enters through stomata • H2O through the xylem in stem • Sugar and Oxygen produced from CO2 and H20 • Oxygen out through stomata • Sugar through plant in phloem Controlling Water Loss • Transpiration – water evaporates from plant’s leaves – Close stomata when leaves start to dry out.