* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Endocrine System - Valhalla High School
Hormonal contraception wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Cryptorchidism wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
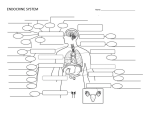
The Endocrine System Glands and Hormones What is your Endocrine system? Your endocrine system consists of your glands and hormones. Like the nervous system, they work to help you maintain your homeostasis. They generally work more slowly, but have longer lasting effects than the nervous system. Endocrine glands These glands are different from salivary or sweat glands. They do not have ducts! The hormones they produce are diffused directly into the blood stream. Glands that have ducts are called exocrine glands. The Pancreas is considered both an endocrine and exocrine gland. (remember digestion!) Glands of the Endocrine system Hypothalamus (important…but not a gland!) The Pituitary gland: Has two parts, anterior and posterior. Thyroid gland Parathyroid gland Adrenal glands Pineal gland Pancreas Gonads: Ovaries and Testes Location of glands in the body Gland Map Hypothalamus Located just anterior of the brain. Does not secrete hormones into the blood stream, but acts as an interface between the nervous and the endocrine system. Since the hypothalamus does not secrete any hormones it is not a gland. It controls the activity of the pituitary through nerves. Pituitary Gland Called the master gland because it secretes hormones that stimulate other glands to secrete their hormones. The anterior pituitary: Prolactin: Stimulates milk production HGH (Human growth hormone): Initiates growth (Too much can lead to the condition known as “giantism”.) TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone): Causes the thyroid gland to release thyroxin. ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic Hormone): Stimulates the adrenal glands to release various hormones. Anterior Pituitary (cont.) This amazing gland also secretes FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone): Stimulates production of mature eggs and sperm LH (Luteinizing Hormone): Stimulates Ovaries and Testes; Prepares uterus for implantation. Pituitary gland (cont.) Posterior pituitary gland. Oxytocin: This is the hormone used to induce labor in pregnant women. Causes the uterine contractions during childbirth Anti-diuretic hormone: Stimulates the reabsorbtion of water in the kidneys. Pineal Gland The pineal gland secretes Melatonin: Melatonin helps regulate our circadian rhythm, or 24-hour wake-sleep cycle. Fun fact! Circadian comes from the latin words: Circa, which means around or about, and dia, which means day. Thyroid gland Secretes the hormone thyroxine which regulates the metabolism of proteins, carbs and lipids. Diseases of the thyroid lead to either hyperthyroidism(too much thyroxine), or hypothyroidism(not enough thyroxine). How do you these conditions would affect a person? Parathyroid Gland Secretes Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) which acts upon bones and kidneys. It helps to regulate calcium levels in the blood. It also is associated with the growth of bone and muscle. Adrenal glands Secretes the hormone: Adrenalin: which acts upon most of the cells in your body. It increases heart rate, breathing rate and increases blood pressure. Initates what is commonly referred to as the “fight or flight” response. It prepares your body for rapid physical activity. The adrenal glands have two parts, and secrete other hormones, but will not concern ourselves with them. Pancreas The pancreas has a section which is called the “islets of langerhans”. The “islets” secrete two hormones that help to regulate blood sugar levels. Insulin is used to reduce the amount of blood sugar. Glucagon is used to increase the amount of blood sugar. Glucagon and Insulin work together in a negative feedback loop. Gonads These are the glands which produce the sex hormones. In females, these are the ovaries, and they secrete the hormones Estrogen and Progesterone. In males, these are the testes, and they secrete the hormone testosterone. Ovaries In women only, these glands secrete Estrogen: Causes the breakdown of the uterine wall, initiating menstruation. Progesterone: Builds up and maintains the uterus wall for embedding of fertilized egg. Associated with secondary sexual characteristics, e.g. body hair, breast enlargement, changes in physical body. Testes In men only, these glands secrete: Testosterone: Responsible for the development and function of male sex organs. Secondary sexual characteristics. e.g. body hair, muscle development, voice change. What to do now? To help remember the roles of all these glands and hormones you will make a set of flash cards. On one side of the card write the name of the hormone. On the other side, write the name of the gland which secretes the hormone AND that hormone’s effect on the body.