* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WHat is Hepatitis? - Tan Tock Seng Hospital
Survey
Document related concepts
Schistosoma mansoni wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Plasmodium falciparum wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Antiviral drug wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
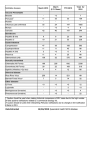
Hepatitis What is Hepatitis? Hepatitis refers to the inflammation of the liver which may lead to liver cirrhosis, cancer and failure. The infections are caused by different viruses which spread by varying means. Hepatitis B and C viruses cause chronic diseases whereas the hepatitis A and E viruses cause acute diseases. Hepatitis B is the most common infection of the liver. Hepatitis can also be caused by many other viruses (e.g Dengue virus), bacterial (e.g Typhcial bacteria) or parasitic (e.g Malaria parasite) and also by some medicines. Symptoms •Jaundice •Dark-coloured urine •Pale stools •Fever •Prolonged fatigue •Poor appetite •Abdominal pain •Nausea and vomiting Visit bit.ly/TTSHDiseases-Conditions for other medical conditions. CARECONNECT (TTSH Patient Experience Centre) Level 1, TTSH Atrium, 11 Jalan Tan Tock Seng, Singapore 308433 TEL 6357 8018 EMAIL [email protected] OPERATION HOURS Monday to Friday 9.00am - 5.00pm Hepatitis Hepatitis A Hepatitis C Hepatitis B Transmission Ingestion of faecal matter from: • Close person-to-person contact with an infected person • Ingestion of contaminated food or drinks Contact with infectious blood, semen, and other body fluids through: • Birth to an infected mother • Sexual contact with an infected person • Sharing of contaminated needles, syringes, or other injection drug equipment • Sharp instrument injuries Treatment • No specific medication • Many recover after two weeks with medications to relieve symptoms and bed rest The treatment of Hepatitis B carriers include: • Diagnosis and evaluation – Blood tests, ultrasonography of the liver and liver biopsy are used to assess the severity of the illness • Supportive therapy – Drugs that boost the immune system to eliminate the hepatitis B virus (e.g. alpha- interferon) or suppress viral replication • Surveillance for liver cancer – The risk is greater amongst Hepatitis B carriers as compared to non-carriers. The patient is subjected to blood tests. Elevated alpha-fetoprotein level is a tumour marker for liver cancer • Alpha-Interferon is the current recommended regime for treatment. It is believed to act by preventing viral replication and boosting the body’s immune system Prevention Hepatitis A is best prevented by vaccination especially if one is travelling to developing countries or have chronic liver disease. Hepatitis B is best prevented by vaccination especially if one is a carrier, immune deficient or requires repeated transfusion of blood due to an illness A vaccine capable of protecting against hepatitis C, is not available Ways of prevention include: • Practising good hygiene • Washing hands with soap before and after meals • Properly cooking shellfish before consumption • Good food handling practices Ways of prevention include: • Avoiding multiple sex partners • Having protected sex • Avoiding the sharing of needles, sharp instruments, toothbrushes with those who are unsure of their Hepatitis status • Avoiding blood, tissue, organs or semen donation if one is a Hepatitis carrier • Going to reliable operators for acupuncture, body piercing or tattooing References: 1. HPB.gov.sg, (2015). Hepatitis A. [online] Available at: http://www.hpb.gov.sg/HOPPortal/dandc-article/534 [Accessed 21 Sep. 2015]. 2. HPB.gov.sg, (2015). Hepatitis B. [online] Available at: http://www.hpb.gov.sg/HOPPortal/dandc-article/536 [Accessed 21 Sep. 2015]. Visit bit.ly/TTSHDiseases-Conditions for other medical conditions. CARECONNECT (TTSH Patient Experience Centre) Level 1, TTSH Atrium, 11 Jalan Tan Tock Seng, Singapore 308433 TEL 6357 8018 EMAIL [email protected] OPERATION HOURS Monday to Friday 9.00am - 5.00pm Scan the QR Code with your smart phone to access the information online or visit http://bit.ly/ TTSHDiseases-Conditions.