* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Newton`s Second and Third Law`s
Artificial gravity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's law of universal gravitation wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
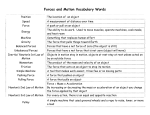
Newton’s Second and Third Law’s Ch 14 Main Idea: As the net force acting on an object increases, the object accelerates more. 1. What affects Acceleration? Force and Acceleration-As a force increases, the acceleration also increases in the same amount. Ex: If you triple a force, the acceleration will also be tripled. Mass and Acceleration- Doubling the mass of an object will decrease the acceleration. Ex: If you tape two toy cars together (increasing the mass), the car will not go as far. 2. Newton’s Second Law of motion: F= m x a 3. How Is Acceleration Calculated? Must know 3 things 1. starting speed 2. new speed 3. amount of time it took for change to happen formula of accelerationo a=F÷m 4. What are Balanced and Unbalanced Forces? Balanced forces- forces that cancel each other out when acting together on a single object. Unbalanced forces- forces that do not cancel each other out when acting together on a single object. 5. How Do Forces Act Between Objects? Action- the force one object applies to a second force Reaction- the force with which an object responds to an action o Newton’s Third Law of motion- For every action, there is an equal reaction. 6. What Is a Simple Machine? Work- using force to move an object Simple machine- a machine with few moving parts to make work easier. Machines lower the force needed to move and lift heavy objects. Levers- has a rigid bar that rests on a pivot point or fulcrum. Fulcrum- pivot point Effort arm- part of lever that applies force to the resistance arm Resistance arm-lever part that applies force to the load the machine acts against. 3 types of Levers 1. first class 2. second class 3. third class They differ in the position of their parts. Wheels and Axles- a large wheel that rotates in a circle around an axle. Pulleys- a wheel with a groove in the rim. A rope fits into the groove. It changes the direction of the effort force. (fixed and moveable) 7. What Is an Inclined Plane? A flat, slanted surface that makes it easier to move heavy objects to higher levels. The slanted surface is the effort arm o Wedges- an inclined plane that is used as a tool for cutting. o Screws- an inclined plane wrapped in a spiral around a cylinder or cone