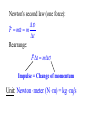* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 6 Class Notes
Virtual work wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Uncertainty principle wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Quantum vacuum thruster wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum operator wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
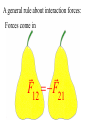
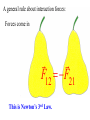
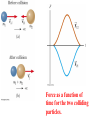
Momentum – Key Ideas Review – If a force Fx is applied to a body over a displacement Dx, the product Fx Dx = (Fcosq)Dx = Work Review – If a force Fx is applied to a body over a displacement Dx, the product Fx Dx = (Fcosq)Dx = Work If the friction force is less than Fx, the work increases the object’s Kinetic Energy 1 1 2 Wnet DKE m mo2 2 2 NOW ask: What is the effect of applying a force over a time interval? Vocabulary: events in which objects apply forces to each other are called INTERACTIONS NOW ask: What is the effect of applying a force over a time interval? Vocabulary: events in which objects apply forces to each other are called INTERACTIONS You predicted the outcomes of some interactions.. How did you do? You predicted the outcomes of some interactions.. How did you do? A general rule about interaction forces: A general rule about interaction forces: Forces come in F12 F21 A general rule about interaction forces: Forces come in F12 F21 This is Newton’s 3rd Law. The product of mass and velocity (a vector quantity) is called momentum (symbol: p) Definition: p m Newton's second law (one force): D F ma m Dt Rearrange: F Dt mD Impulse = Change of momentum Newton's second law (one force): D F ma m Dt Rearrange: F Dt mD Impulse = Change of momentum Unit: Newton meter (N m) = kg m s The impulse is the area under the force vs. time curve. The average force gives the same impulse to the object in the time interval Δt as the real time-varying force. Conservation of Momentum The principle of conservation of momentum states when no external forces act on a system consisting of two objects that collide with each other, the total momentum of the system remains constant in time. Specifically, the total momentum before the collision will equal the total momentum after the collision. Conservation of Momentum Mathematically: m1 m22 m1 f m22 f Momentum is conserved for the system of objects. The system includes all the objects interacting with each other. Assumes only internal forces are acting during the collision. Can be generalized to any number of objects. Force as a function of time for the two colliding particles. In all collisions, total momentum is conserved. We consider two types of collisions in one dimension: 1. Totally elastic 2. Totally inelastic Perfectly Inelastic Collisions When two objects stick together after the collision, they have undergone a perfectly inelastic collision. m1 m22 m1 f m22 f 1 1 1 1 m1 m22 m1f m22 f 2 2 2 2 Final velocities: f m1 m2 2m2 2i m1 m2 m1 m2 f 2m1 m m1 2 2i m1 m2 m1 m2 Conservation of momentum becomes m1i m2i2 m1 m2 f Elastic Collisions Both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved. m1 m22 m1 f m22 f 1 1 1 1 m1 m22 m1 f m22 f 2 2 2 2 Final velocities: m1 m2 2m2 f 2i m1 m2 m1 m2 2m1 m2 m1 f 2i m1 m2 m1 m2