* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download secondary growth
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
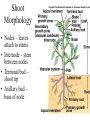
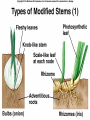
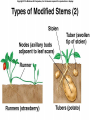
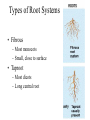
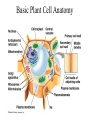
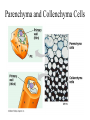
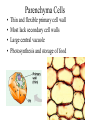
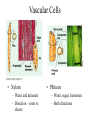
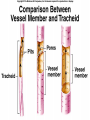
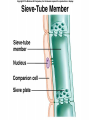
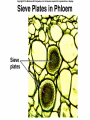
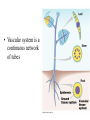
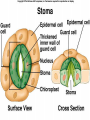
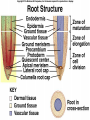
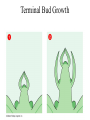
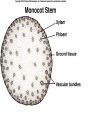
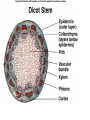
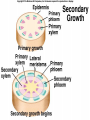
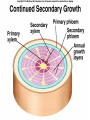
Angiosperms • Flowering plants • Most diverse group of plants (~275,000 species) • Divided into two taxonomic groups – Monocots – Dicots Shoot System • Vegetative – stem and leaves – Photosynthesis • Floral – end in flowers – Reproductive structures Shoot Morphology • Nodes – leaves attach to stems • Internode – stem between nodes • Terminal bud – shoot tip • Axillary bud – base of node Bulbs and Rhizomes Runners and Tubers Tendrils and Cladophylls Leaf Morphology • Monocots – Parallel veins • Dicots – Multi-branched network – Palmate or pinnate veins Blade Petiole Roots System • Anchor plant • Absorb and conduct water and nutrients • Store food Types of Root Systems • Fibrous – Most monocots – Small, close to surface • Taproot – Most dicots – Long central root Increased Surface Area • Root hairs – Extensions off of surface root cells • Mycorrhizae – Symbiotic association between roots and fungi Specialized Roots • Store food – Thickened taproot – Example – carrot • Adventitious roots – Grow from stems – Example – prop roots of corn Basic Plant Cell Anatomy Parenchyma and Collenchyma Cells Collenchyma Cells • • • • Thick primary cell walls Most lack secondary cell walls Stacked cylinders Support young plants Parenchyma Cells • • • • Thin and flexible primary cell wall Most lack secondary cell walls Large central vacuole Photosynthesis and storage of food Sclerenchyma Cells • • • • Rigid secondary cells wall with lignin Protoplast die at maturity Fibers – long thin bundles Sclerids – short irregular shapes Vascular Cells • Xylem – Water and minerals – Direction – roots to shoots • Phloem – Water, sugar, hormones – Both directions Xylem Structure Tracheids – Bundles of small diameter tubes – Pits in end wall allows water and minerals to flow from cells to cell Xylem Structure Vessel elements – Large diameter – End wall either absent or perforated • Pits allow water and minerals to flow between vessel element and tracheid • Vessel element die after development and add support to the plant Phloem Structure • Sieve-tube element – End wall is perforated forming sieve plate – Lose most of their internal components – only has plasma membrane, few mitochondria and some endoplasmic reticulum • Companion cells – Support and nourish adjacent sieve-tube elements • Vascular system is a continuous network of tubes Leaf Anatomy Leaf Summary • Stoma – Controls transpiration (water loss through leaves) • Spongy/palisade layer – Exchange of gases – Photosynthesis • Epidermis – Transparent – Wax coating to prevent water loss • Vascular bundle – Brings water and mineral to leaf through xylem – Sends sugars to roots through phloem Stoma Plant Tissues • Dermal – Outside covering – Epidermis • Stems and leaves – waterproof wax coating • Roots – root hairs – absorb water – Periderm • Bark • Ground – Photosynthesis, support, storage • Vascular – Transport • Xylem – water and minerals • Phloem – water, sugar, amino acids, hormones Plant Growth • Apical meristem – End of roots and shoots – Increases length – primary growth • Lateral meristem (cambia) – Cylinder of cells along roots, branches and stems – Increases width – secondary growth Root Growth Terminal Bud Growth Monocot Stem Dicot Stem Dicot Secondary Growth Annual Growth Rings