* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHAPTER 17
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Optical rectenna wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
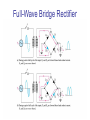
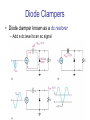
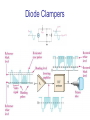
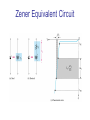
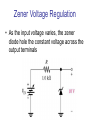
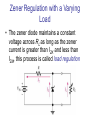
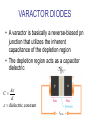
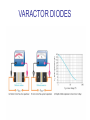
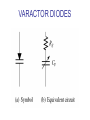
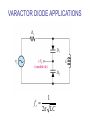
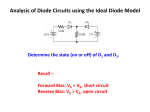
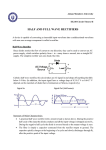
CHAPTER 17 DIODES AND APPLICATIONS HALF-WAVE RECTIFIERS • The basic DC power supply – The dc power supply converts the standard 220 V,50 Hz into a constant dc voltage – They consist of three parts : Rectifier, Filter, and Regulator – The dc voltage produced by a power supply is used to power all types of electronic circuits, such as television receivers, stereo systems, VCRs, CD player Power supply Figure 17-1 The Half-Wave Rectifier Figure 17-2 Average Value of the Half-wave output voltage VAVG=Vp (out) / Effect of Diode Barrier Potential on Half-Wave Rectifier Output Voltage • During the positive half-cycle, the input voltage must overcome the barrier potential before the diode becomes forward-biased Vp (out) =Vp (in) - 0.7 V Figure 17-5 Peak Inverse Voltage (PIV) • The maximum value of reverse voltage, sometimes designated as PIV, occurs at the peak of each negative alternation of the input cycle when the diode is reversebiased Figure 17-7 FULL-WAVE RECTIFIERS • The full-wave rectifier is the most commonly used type in dc power supplies • allowing unidirectional current to the load during the entire input cycle differ from the half-wave rectifier that allows only during one-half of the cycle Figure 17-9 Average Value of the Full-wave rectified output voltage VAVG= 2Vp (out) / Center-Tapped Full-Wave Rectifier • Using two diode connected to the secondary of a centertapped transformer – At the positive half-cycle • Forward-biases the upper diode D1 • Reverse-biases the upper diode D2 – At the negative half-cycle • Reverse-biases the upper diode D1 • Forward-biases the upper diode D2 Center-Tapped Full-Wave Rectifier Effect of the Turn Ratio on FullWave Output Rectifier • If the turn ratio of the transformer is 1:1, the output of the rectifier is equal to ½ of the input voltage Vp • Owing to the voltage input is approximately equal to the output voltage, we must use the step-up transformer Peak Inverse Voltage (full-wave rectifier) VD 2 Vp (sec) 2 Vp ( out) Vp (sec) 2 Vp (sec) Vp (sec) 2 Vp (sec) 2 2Vp (sec) PIV Vp (sec) 2Vp ( out) Full-Wave Bridge Rectifier Bridge Output Voltage PIV Vp (sec) Vp ( out) POWER SUPPLY FILTER AND REGULATORS • After passed the rectifier, the output of the power supply is filtered for reduce the ripple, on the other hand, for make an output smoothly – Capacitor-Input filter – Ripple Voltage • The voltage which change due to charging and discharge of the capacitor is called “ripple voltage” Ripple Factor (r) • Ripple factor is the ratio of the Vr to VDC, expressed as : Vr r 100% VDC NOTE: the frequency in the full-wave rectifier is twice of the half-wave rectifier Ripple Voltages for half-wave and full-wave Surge Current in the CapacitorInput Filter IC Regulators • An integrated circuit regulator is a device that is connected to the output of a filtered rectifier and maintains a constant output voltage • The capacitor-input filter reduces the input ripple to the regulator to an acceptable level and it is combined in IC regulator. • The most IC regulators have three terminal – Input terminal – Output terminal – Reference terminal IC Regulators Basic regulated power supply Percent Regulation • Line regulation – Specifies how much change occurs in the output voltage for a given change in the input voltage Line regulation = • Load regulation ∆VOUT ∆VIN 100% – Specifies how much change occurs in the output voltage over a certain range of load current value VNL- VFL Load regulation = VFL 100% Diode Limiting and Clamping Circuits • Diode Limiters – Diode limiters (clipper) cut off above or below specified levels Vout RL Vin RS RL Diode Limiting and Clamping Circuits • Diode Limiters – Adjustment of the limiting level Diode Clampers • Diode clamper known as a dc restorer – Add a dc level to an ac signal Diode Clampers ZENER DIODES • The zener diode is a silicon pn junction device and operate in the reverse breakdown region symbol Zener Breakdown (Vz) • Two types of reverse breakdown in a zener diode – Avalanche • also occures in the rectifier diode – Zener • Occurs in a zener diode at low reverse voltages NOTE : Zeners with breakdown voltage of 1.8 to 200 V are commercially available Breakdown Characteristic Zener Equivalent Circuit Zener diode impedance • The ration of ∆Vz to ∆Iz is the zener diode impedance Zz = ∆VOUT ∆VIN • Normally, ZZ is specified at IZT • ZZ is approximately constant over the full range of reverse-current values Zener Voltage Regulation • Zener diodes can be used for voltage regulation in noncritical low-current applications Zener Voltage Regulation • As the input voltage varies, the zener diode hole the constant voltage across the output terminals Zener Regulation with a Varying Load • The zener diode maintains a constant voltage across RL as long as the zener current is greater than IZK and less than IZM, this process is called load regulation Percent Regulation • Line regulation – Specifies how much change occurs in the output voltage for a given change in the input voltage • Load regulation – Specifies how much change occurs in the output voltage over a certain range of load current value VARACTOR DIODES • A varactor is basically a reverse-biased pn junction that utilizes the inherent capacitance of the depletion region • The depletion region acts as a capacitor dielectric A C d dielectric constant VARACTOR DIODES VARACTOR DIODES VARACTOR DIODE APPLICATIONS fr 1 2 LC LEDs and PHOTODIODES • There are two types of optoelectronic devices – The Light Emitting Diode (LED) – The photodiode (light detector) The Light Emitting Diode (LED) • When the device is forward-biased, electrons across the pn junction from the n-type material and recombine with the holes in the p-type material • When recombination takes place, the recombining electrons release energy in the form of heat and light The Light Emitting Diode (LED) • The semiconductive materials used in LEDs are gallium arsenide(GaAs), galium arsenide phosphide (GaAsP), and Gallium phosphide (GaP) • Silicon and Germanium are not used because they are very poor at producing light • GaAs LEDs emit infrared (IR) radiation • GaAsP produces either red or yellow visible light • GaP emits red or green visible light The Light Emitting Diode (LED) electroluminescence symbol The Light Emitting Diode (LED) The Light Emitting Diode (LED) Applications The Photodiode • The photodiode is a pn junction device that operates in reverse bias The Photodiode The Photodiode operation The Photodiode Applications The diode data sheet TROUBLESHOOTING Homework • Basic problems – 1, 6, 12,16 12 16