* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 3 Study Guide
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
Division by zero wikipedia , lookup
P-adic number wikipedia , lookup
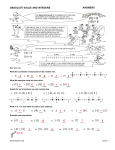
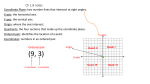
Unit 2 – Integers, Number lines, the Coordinate Plane Student Study Guide SpringBoard Lesson Number Learning Targets 6.NS.C.5 KDE Learning TargetsI can identify an integer and it’s opposite. (K) I can use integers to represent quantities and explain the meaning of zero in real world situations (above/below sea level, etc.) (R) Example: Which integer has an opposite of 9? Example: Which situation would NOT be represented by a negative integer? A. B. C. D. an increase of 6 pounds a loss of $45.00 a decrease of 12 yards 4 inches below normal 7-1 Unit 2 – Integers, Number lines, the Coordinate Plane Student Study Guide Learning Targets SpringBoard Lesson Number 6.NS.C.6 - KDE Learning Targets for Number Lines I can plot a number and its opposite on a number line and show that they are equidistant from zero. (K) I can find and place integers and other rational numbers on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram. (K) I can explain that the opposite of the opposite of a number is the number itself. (R) Example: Look at the number line. Estimate the value of point P to the nearest ¼ . Explain how you know. Example: What is the opposite of point P? _______. Plot the opposite of point P as point Q on the number line above. Example: What is the opposite of – ( ̶ 6). 6.NS.C.6 - KDE Learning Targets for Coordinate Plane I can use the signs and integers of the coordinates in an ordered pair to find its location in a coordinate plane (K) I can explain that when two ordered pairs only have different signs, the locations of the points are reflections of each other across one or both axes. (R) Example: What is the coordinate pair of point A on the grid below? Example: Name the ordered pair for point D above. Reflect point D across the x-axis. What is the name of the coordinate pair of point D’s reflection across the x-axis? 7-1 9-1 Unit 2 – Integers, Number lines, the Coordinate Plane Student Study Guide SpringBoard Lesson Number Learning Targets 6.NS.C.7 KDE Learning TargetsGiven a statement of inequality, I can describe how the position of two numbers on a number line will compare. (R) I can write and explain the meaning statements of inequality in real-world contexts. (R) I can identify absolute value of rational numbers as its distance from zero on a number line. (K) I can describe absolute value as the magnitude of the number in a real world situation. (R) I can use absolute value to describe and make comparisons between rational numbers in real world contexts. (R) Example: True or False: - 3 < - 7 Example: Place these integers in order from least to greatest. 3, −7, 0, 4, −1 Example: What is the absolute value of these numbers? 4, -4, 8, -7, and 0. What does absolute value of a number mean? Example: A submarine is 250 feet below the surface of the ocean. What integer represents its depth? Example: The wind-chill temperature on Tuesday for four cities are −8.2⁰F, −7.7⁰F, −5.8⁰F, and −6.2⁰F. Place these numbers in order from greatest to least. 7-1 7-2 Unit 2 – Integers, Number lines, the Coordinate Plane Student Study Guide Learning Targets SpringBoard Lesson Number 6.NS.C.8 KDE Learning TargetsI can graph points in all four quadrants of the coordinate plane to solve real-world and mathematical problems. (R) I can use absolute value to find the distance between two points with the same x-coordinate or the same y-coordinate. (R) Example: What point is the ordered pair for Point B in the coordinate plane below? Example: In the coordinate plane, what is the distance between ( ̶ 3, 5 ) and ( ̶ 3, ̶ 8) ? 9-2