* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Enteric Bacteria
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Foodborne illness wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenic Escherichia coli wikipedia , lookup
Cryptosporidiosis wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
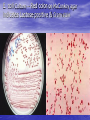
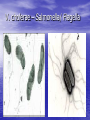
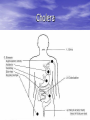
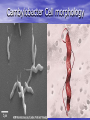
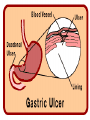
Enteric Bacteria Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine University of Jordan Enteric Bacteria • General Characteristics: Gram-ve Bacilli, Facultative Anaerobes, Oxidase-negative.. Part Intestinal Normal Flora.. Humans, Animals, Birds.. Common Waste water, Natural Water, Soil, Vegetation. • Opportunistic Pathogens/Obligate Pathogens.. Enterotoxins, Endotoxins, Capsules, Flagella, Pili • Coliform Group: 1. Escherichia coli: Urinary Tract Infect (40-70%)..Single Organism, Septicemia, Neonatal Meningitis, Wounds. Diarrheagenic E coli strains: - Enteropathogenic:Infants.. mild-chronic diarrhea, Enterotoxigenic.. Heat-Labile/Stable Enterotoxin, Watery diarrhea.. More Children than Adults.. Travelers diarrhea..Contamination Water/Vegetables / Fresh food Coli-form group-2 dairy products ..Mostly Self-limited.. No need for Antibiotics treatment. - Enterohaemorrhagic .. Common in intestinal Cattels, verotoxins.. Contamination Ground meat/Hamburger,Dairy products..Bloody diarrhea.. Haemolytic-ureamic syndrome, pertonitis, Kidney failure..Outbreaks of infections. • E. coli is used as indicator for detection of water & Food fecal contamination. 2. Klebsiella-Enterobacter –Serratia species: UTI, Septicemia, Wounds.. Rare Meningitis.. Common Hospitalized patients. • K. pneumoniae.. Large polysaccharide.. capsule.. Nosocomial Pneumonia. E. coli Culture – Red color on MaConkey agar indicates Lactose-positive & Gram-stain E.coli-Flagella-Fimbriae-Pili Klebsiella pneumonia-Capsule Coliform group-3 • E.coli, Klebsiella-Enterobacter –Serratia spp.. Lactose+ve , urease-ve & oxidase-negative.. • Klebsilla spp. often encapsulated.. Non-motile • 3. Proteus-Providencia-Morganella species: Lactose-ve & urease positive.. cause UTI, Septicemia, Wounds.. Commonly in Hospitalized patients. • Lab Diagnosis: All Enteric bacteria grow on MacCokeny-, Blood-, CLED-agar. Full identification done using Biochemical Tests.. Antibiotic Susceptibility must be done. 4. Pseudomonas group • Gram-ve bacilli, Oxidase-positive, Single polar • flagellum,Fimbriae, obligate aerobe, widely distributed in human intestine, animal, plants, environment & water. Survive in disinfection solutions.. 70% Alcohol..contaminate Hospital sinks & equipments. P. aeruginosa: Most common causes of human & animal infections.. Produce several hemolyticprotolytic enzymes, toxins, fluorescent pigmentspyocyanin / Burn-Blue Green Pus.. can overcome host defenses.. Wounds,, External Otitis Media, Septicemia, Pneumonia, UTI, Nosocomial Infection, Mutlidrug Resistance.. Intrinsic-R to many antibiotics..Common Nosocomial/ opportunistic Pathogen. 5-Salmonella group • Gram-ve bacilli.. Lactose-ve, urease-ve, Motile, • • Facultative Anaerobes.. Endotoxin/LPS, Cytotoxin.. common in Nature.. Humans, most domestic & wild Animals, Birds, Reptiles ..Develop of specific antibodies during invasive infection against their O/HAntigens.. Salmonellosis: 1-Gastroenteritis/ Food-poisoning Salmonella: S. enterica/ enteritidis.. Numerous Serotypes.. Common Farm Chickens, Pets.. Contamination Chicken MeatEggs, Water.. Fecal-Oral Infection.. Incub. 8-24 h.. Mild-Severe Diarrhea, Vomiting, Fever.. Mostly SelfLimited in Adults. More severe infection in children.. Septicemia-Meningitis in Immuno-compromised Pat. V. cholerae – Salmonella/ Flagella Hekton–Enteric agar for Isolation of Salmonella (E.coli-Salmonella growth) Typhoidal Salmonella 2- Typhoidal Salmonella: Human Enteric Fever.. Salmonella enterica /subtype Typhi & Paratyhi A, B, C., Fecal-Oral route, Fecal water contamination or drinks/ Fresh Food.. Intestine..Blood, Meningis,Urinary tract.. Incubation Period 1-3 Weeks, high Fever up to 42, Diarrhea, constipation, Septicemia, Meningitis, Hepatospenomegaly, Intestinal Perforation.. Healthy Carriers.. Mostly females in Gallbladder.. Less Intestine.. Repeat chronic infection.. Stool Excretion..single cases and community water outbreaks. • Lab Diagnosis: Culture Feces, blood, Urine, CSF, Selective Media.. Serological Widel Test for detection of specific antibodies against O & H antigens ( Titer > 160 ).. Antibiotic, Human vaccine available. 6-Shigella group • Shigella species.. Gram-ve bacilli, cause Only human • • disease.. Endo/Enterotoxins.. Susceptible to Dryness, Acid, Low-High Tempt. Fecal-Oral infection.. Water, fresh Vegetations, Common serotypes, S. Sonnei, Sh.boydii Sh. flexneri Purulent-BloodyDiarrhea..Fever abdominal pain..Recovery 2-4 days with treatment.. No chronic healthy Carriers. S.dysenteriae.. Enterotoxin (Neurocytotoxin), Severe Necrosis, high Fever, Severe Purulent-Bloody-Diarrhea & Abdominal Cramps, CNS affection.. Rare Septicemia. Lab Diagnosis: Feces Culture.. S-S Agar, Hecton – Enteric Agar.. Recommended Antibiotic Treatment, Control Sanitation & hygiene.. water, fresh Food. 7-Vibrio cholerae • Gram-ve Vibrios.. Oxidase-positive & Motile, Aerobic • • • Alkaline Medium (pH >8-9)..Killed in low acidity.. Survive in saline water for long time.. Endemic In India/Bangladish.. Highly infectious.. Epidemic Human Outbreaks.. Water, Fresh Green leaves & Food V. cholera-01: Type V. cholera El-Tor.. Only Human.. Fecal-Oral Infection, multiply small intestine..release Cholera-toxin.. Heat-labile enterotoxin, Incub. 8-48 h.. Severe Watery Diarrhea, Dehydration, Shock.. Death. Within 24 hrs..No invasive infection. Lab Diagnosis: Feces Culture.. Selective TCBS agar. Treatment: Replacement Fluids & Electrolytes.. Antibiotic.. Public Heath Measurements.. Human Vaccine recommended for Refuges & Army. Cholera TCBS agar for isolation of V.cholerae/ Salmonella–Shigella agar (Lactose-negative) 8-Brucella species • Brucellosis/Malta Fever.. Gram-ve coccobacilli..Non- motile, Intracellular, Endotoxins.. Primarily a Pathogens of Animals (Zoonosis), Localized Infection in reproductive Organs.. Sepsis, Abortions. • Br. abortus (Cattel), Br. melitensis (Goats/Sheep). • Human Brucellosis/Malt Fever : Mostly Br. melitensis.. Rare Other species in Jordan. • Transmitted to Humans.. Unpasteurized Milk/Milk Products.. Cheese, Direct Animal Contact.. Few Cells Enter Through GI, Skin Abrasions, Eye, Inhalation/Droplets.. Intracellular ..Lymphatic System.. Septicemia, Meningitis, Chronic disease Brucella-2 • Clinical Features: Incub. 1-6 Weeks.. Intermittent • • • • fever, headaches, fatigue, joint and bone pain, GI Symptoms, Sweats, Back Pains, Acute- SubacuteChronic Infections. Common Complications: Arthritis, Meningitis-CNS, Osteomylitis, Localized Lesions in any body part. Lab Diagnosis: Culture Blood, CSF, Bone marrow (Chronic Infection).. Brucella agglutination Test.. Specific Antibodies Treatment: 6-8 Weeks with Antimicrobial drugs Prevention: Control Brucella in Animals by slaughtering infected animals .. Animal Vaccination, Pasteurization Milk/ Milk Products 9-Campylobacter Species • Campylobacter jejuni , is Gram-negative slender, • • • • curved, motile by one/ two polar Flagellium, Spiral form, Grow Microaerophilic at 37-42..Normal Intestines flora all Birds, Animal..dogs, cats.. contaminated often Chicken Meat, Milk, food, water. It is primarily an animal pathogen causing abortion and enteritis in sheep and cattle. Common cause of food-poisoning, important enteric pathogen since 1976.. In Western Countries. C. jejuni .. Incubation 2-5 days..release Cytotoxins.. Intestinal inflammation..causes mild-moderate bloodywater diarrhea, Children.. , Other symptoms often present are fever, abdominal pain, nausea, headache and muscle pain..Rare Sepsis & complication Arthritis, Diagnosis: Stool culture .. Selective culture Media Cambylobacter Cell morphology 10-Helicobacter Species • Helicobacter pylori is a spiral shaped • • bacterium..One polar flagella.. Colonize only mucus lining cover mucosa of Gastric Antrim.. and duodenum.. Produce extensive Urease..Split urea to Ammonia..release Cytotoxin.. Mild-sever ulceration The stomach is protected from its own gastric juice by a thick layer of mucus that covers the stomach lining. Helicobacter colonize and infect only humans worldwide, where up to 10% of children & 80% of adults can have evidence of an H. pylori infection usually without having any clinical signs or symptoms. Helicobacter Helicobacter Species-2 • Common symptoms: gastritis or peptic ulcer • • • • /Stomach.. duodenal ulcers ..burning, Abdomen Pain, Nausea, Vomiting. Persistence of ulcers .. Development of Stomach Cancer and Lymphoma..1-3% H. pylori can be successfully eradicated using a combination of certain antibiotics and medicines that suppress stomach acid production. Common Reoccurrence of infection & disease Diagnosis: Urea Breath Test, Culture Stomach Biopsy.. Culture on Selective Medium.. 42C.. Serological test for specific antibodies is not significant