* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Viral Detection
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Influenza A virus wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Bovine spongiform encephalopathy wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Surround optical-fiber immunoassay wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
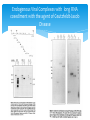
Viral Detection By: Douglas Tran Endogenous Viral Complexes with long RNA cosediment with the agent of Ceutzfeldt-Jacob Disease Past research States Prion hypothesis and past research of no past viral genetic material detected States the fact that mitochondrial DNA has been found in subsequent studies States that long RNAs cores were also detected Very similar to retroviral cores Endogenous Viral Complexes with long RNA cosediment with the agent of Ceutzfeldt-Jacob Disease CJD Retroviral Theory Strain variation, exponential replication, tissue specificity, latency, resistance to treatment, and noninflammatory response LTRs detection experience found LTRs present in infectious samples Endogenous retroviral intracisternal A particle (IAP) genome were identified by using cDNAs that were created from the LTRs of infectious factions Endogenous Viral Complexes with long RNA cosediment with the agent of Ceutzfeldt-Jacob Disease IAP RNA cosediement found (The RNA that is being detected) IAP are a class of retrovirus In Infectious sample In non-infectious sample IAP are highly resistant to forms of treatment like SDS and chaotropic salts High resistance is due to IAP gag proteins Isolation of this gag protein would help solidify the idea of virus particle, not just random IAP RNA Endogenous Viral Complexes with long RNA cosediment with the agent of Ceutzfeldt-Jacob Disease Source of materials and purification of CJD infectivity Syrian hamster IAP genome Polyclonal antibodies that bind the IAP gag protein 12 CJD infected hamster brains Purification: samples made devoid of PrP-res Samples also treated with nuclease (allows for isolation of nuclease resistant genetic material) Extraction of RNA Elimination of DNA in sample via various methods (DNAase) Endogenous Viral Complexes with long RNA cosediment with the agent of Ceutzfeldt-Jacob Disease RNA/PCR amplification of IAP sequences Usage of various IAP primers for the production of subsequent cDNA syntheses IAP RNA from cells -> cDNA-> DNA amplification via IAP primer Probe hybridization to Southern Blots DNA probes Generated from recombinant clone of Syrian Hamster IAP Western blot Polyclonal rabbit anti-mouse IAP gag antibodies Endogenous Viral Complexes with long RNA cosediment with the agent of Ceutzfeldt-Jacob Disease Endogenous Viral Complexes with long RNA cosediment with the agent of Ceutzfeldt-Jacob Disease Endogenous Viral Complexes with long RNA cosediment with the agent of Ceutzfeldt-Jacob Disease • Discussion: • Was able to isolate both IAP RNA and RNA gag in infectious samples • Both are resistance to degradation of nuclease, which shows characteristic of retroviral • Results refuted the assumption of prion infection being devoid of nucleic acid • ~6kb IAP sequences • No clear evidence of a CJD specific sequence of IAP RNA • If IAPs are involved with the CJD nucleic acid, it is either co-packed in the core or uses IAP products to proliferate • Second theory: Completely independent CJD viral complex, only similar to IAP • Supported by presence of gag-like proteins Viral Particles are required for infection in neurodegenerative Creuzfeldt-Jakob disease States the assumption of virus infectivity theory Characteristic of the CJD infectious agent Core-like viral density of 1.27-1.28 g/cc Viral size of 120S and a diameter of ~30nm >99% of starting prion protein can be separated from the viral agent Primary investigation: Separation and isolation of the primary components of the viral protein (testing different methods) PrP Nucleic acid-binding proteins Gag protein Viral Particles are required for infection in neurodegenerative Creuzfeldt-Jakob disease Method Centrifuge isolation of supernatant and pellets after elimination of the majority of PrP Immunoblots (Western blot method used for protein isolation) Polyclonal antibodies Viral Particles are required for infection in neurodegenerative Creuzfeldt-Jakob disease Viral Particles are required for infection in neurodegenerative Creuzfeldt-Jakob disease Viral Particles are required for infection in neurodegenerative Creuzfeldt-Jakob disease Viral Particles are required for infection in neurodegenerative Creuzfeldt-Jakob disease Viral Particles are required for infection in neurodegenerative Creuzfeldt-Jakob disease Results show that a specific nucleic acid and one or more binding proteins are intrinsic components of the CJD virus Independently have low infectivity, but together form a complex that is the main infective agent Infectivity is not Prp dependent, SDS treatment eliminates the majority of Prp, but infectivity is still high Gdn-HCI treatment who greatly lower infectivity due to elimination of the viral components There is still retention of PrP in Gdn-HCI samples Nuclease resistant circular DNAs copurify with infectivity in scrapie and CJD Begins paper by stating examples of virus that have similar and/or the same characteristics of CJD viral infection States theory involving PrP as the viral receptor and that after interaction with virus it causes the formation of PrP-res Lists the common flaws in Prion Hypothesis Nuclease resistant circular DNAs copurify with infectivity in scrapie and CJD Primary goal: Isolation and identification of circular ssDNA via generalized detection method Ф29 polymerase to enhance the replication of the circular ssDNA Circular DNA hypothesis is based off CJD’s similarity with Torgue tenovirus, which has circular DNA It is also based on Circular DNA’s ability to cause physical generation like the formation of mouse tumors Nuclease resistant circular DNAs copurify with infectivity in scrapie and CJD Infectious material: Three source that underwent PrP depletion procedures Murine N2a neuroblastoma (22L) Hamster brain (263K) Japanese FU-CJD patient (FU-CJD) Nucleic acid extractions Usage of Proteinase K for digestion of endogenous or added nucleases Used purification method for digested genetic material Nuclease resistant circular DNAs copurify with infectivity in scrapie and CJD Ф29 polymerase and ssDNA chromatography Allow for the amplification of circular ssDNA from the digested nucleic acid RNA and RNAase inhibited the effects of Ф29 polymerase ssDNA was isolated from these factors and dsDNA before replication Restriction enzyme analysis, PCR and sequencing Digestion of the Ф29 polymerase product -> PCR proliferation -> sequenced Nuclease resistant circular DNAs copurify with infectivity in scrapie and CJD Nuclease resistant circular DNAs copurify with infectivity in scrapie and CJD Nuclease resistant circular DNAs copurify with infectivity in scrapie and CJD Nuclease resistant circular DNAs copurify with infectivity in scrapie and CJD Nuclease resistant circular DNAs copurify with infectivity in scrapie and CJD Nuclease resistant circular DNAs copurify with infectivity in scrapie and CJD Demonstration of two new circular DNAs that is in high concentration in TSE particles All three strains tested strongly positive for Sphinx 1.8kb and 2.4kb, which show a clear viral plasmid structure Both are passed down to daughter cells Both are also present in uninfected brains, but the concentration in infected brain is x2,500 higher Positive control: Mitochondrial DNA was used In essence, Sphinx DNA is viral, their actual role is up for further investigation