* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Marketing
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Internal communications wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Brand equity wikipedia , lookup
Market analysis wikipedia , lookup
Customer experience wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Sports marketing wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
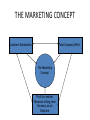
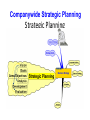
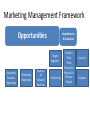
Ashesi University COURSE TITLE : MARKETING SEMESTER : FIRST, 2011/201 MODULE 1: Introduction to Marketing Lecturer: Ebow Spio Agenda for Day One 1. 2. 3. 4. Welcome and Introduction Discuss course outline & work program Grading System Presentation of Learning Effectiveness Research 5. Introduction to the subject Most People Learn ……. Percentage of material/thing learnt Learning activity 10% Of what they read 20% Of what they hear 30% Of what they see 50% Of what they see and hear 70% Of what they talk over with others 80% Of what they use and do in real life 95% Of What they teach someone else Source: Attributed to William Glasser; quoted by Association for Supervision & Curriculum Development Guide 1998. Grading System Raw Score Grade Credit Code Interpretation 80-100 A 4.0 Excellent 75-79 B+ 3.5 Very Good 70-74 B 3.0 Good 65-69 C+ 2.5 Average 60-64 C 2.0 Fair 50-59 D+ 1.5 Barely Satisfactory 50-54 D 1.0 Weak Pass Below 50 E 0 Fail Grading System : Class Designation CGPA Class Cumulative Grade Point Average 1st Class 3.6-4.0 2nd Class (Upper Division) 3.0-3.5 2nd Class ( Lower Division) 2.5-2.9 3rd Class Division 2.0-2.4 Pass 1.0-1.9 Fail Less 1.0 Learning Objectives 1. Define marketing and outline the steps in the marketing process 2. Explain the importance of understanding customers and the marketplace 3. Discuss the marketing management orientations that guide marketing strategy 4. Explain companywide strategic planning in its four steps 5. Discuss how to design business portfolios and develop growth strategies 6. Explain content and process for developing and implementing a marketing strategy and plans 7. Appreciate the benefits of marketing to consumers, firms and society 8. Know the criticisms leveled against marketing 9. Have an idea of Marketing activities 10. Role and Capabilities of a Marketing Professional of the Future 1-2 Defining Marketing • “Marketing is a social and managerial process buy which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating and exchanging products and value with others” (Kotler et al. 2003) • “Marketing is the management process which identifies, anticipates and supplies customer requirements efficiently and profitably” (Chartered Institute of Marketing 1976) • “Marketing is the process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion and distribution of ideas, goods and services to create exchange and satisfy individual and organisational objectives” (AMA 2004). • “Marketing is the process of achieving corporate goals through meeting and exceeding customer needs better than the competition” (Jobber 2003). • “Marketing is an organizational function and a set of processes for creating, communicating, and delivering value to customers and for managing customers relationships in ways that benefit the organization and its stakeholders” What is marketing? AMA “Marketing is the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large” (American Marketing Association, 2008) 8 What is Marketing? CIM UK • (New) Proposed definition: "The strategic business function that creates value by stimulating, facilitating and fulfilling customer demand. It does this by building brands, nurturing innovation, developing relationships, creating good customer service and communicating benefits. By operating customercentrically, marketing brings positive returns on investment, satisfies shareholders and stakeholders from business and the community, and contributes to positive behavioural change and a sustainable business future". Defining Marketing Marketing is the delivery of customer satisfaction at a profit. The goal of Marketing • Attract new customers by promising superior value • Keep and grow current customers by delivering satisfaction. The Marketing Process 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Understand the marketplace and customer wants and needs Design a customer-driven marketing strategy Construct a marketing plan that delivers superior value Build profitable relationships and create customer satisfaction Capture value from customers to create profit and customer equity 1-5 Understanding the Marketplace and Customer Needs Customer Needs, Wants, and Demands • a need is a state of felt deprivation of some basic satisfaction • wants are desires for specific satisfiers of these deeper needs • demands are wants for specific products that are backed by an ability and willingness to buy them 1-6 Understanding the Marketplace and Customer Needs Market Offerings—Products, Services, and Experiences Market offerings are some combination of products, services, information, or experiences offered to a market to satisfy a need or want Exchange is the act of obtaining a desired object from someone by offering something in return Relationships consist of actions to build and maintain desirable relationships 1-8 Marketing thought: what do you sell? 14 Understanding the Marketplace and Customer Needs Markets are the set of actual and potential buyers of a product Marketing system consists of all of the actors (suppliers, company, competitors, intermediaries, and end users) in the system who are affected by major environmental forces • Demographic • Economic • Physical • Technological • Political–legal • Socio-cultural 1-12 Marketing Management Orientations • • • • • Production concept Product concept Selling concept Marketing concept Societal concept 1-18 Marketing Management Orientations Production concept is the idea that consumers will favor products that are available or highly affordable “If we can make, it will sell” is management thinking characteristic of the production concept. • Run a risk of focusing narrowly on own internal operations. 1-19 Marketing Management Orientations Product concept is the idea that consumers will favor products that offer the most quality, performance, and features for which the organization should therefore devote its energy to making continuous improvements The product concept also can lead to marketing myopia. For instance, railroad management once thought that users wanted trains rather than transportation and overlooked the growing challenge of airlines, buses, trucks, and automobiles. 1-20 Marketing Management Orientations Selling concept is the idea that consumers will not buy enough of the firm’s products unless it undertakes a large scale selling and promotion effort. • Typically practiced with unsought goods— • Firms practice the selling concept when they have overcapacity • The aim is to sell what they make rather than make what the market wants. • It focuses on creating sales transactions rather than on building long-term, profitable relationships with customers. 1-21 Marketing Management Orientation Marketing concept is the idea that achieving organizational goals depends on knowing the needs and wants of the target markets and delivering the desired satisfactions better than competitors do. Expression of Marketing Concept • “We’re not satisfied until you are” (GE); • “Let us exceed your expectations” (Celebrity Cruise Lines). • “To do all in our power to pack the customer’s dollar full of value, quality, and satisfaction.” JC Penney • “I do not consider a sale complete until goods are worn out and the customer still is satisfied. We will thank anyone to return goods that are not perfectly satisfactory. . . . Above all things we wish to avoid having a dissatisfied customer.” L.L. Bean (www.llbean.com 1-22 THE MARKETING CONCEPT Customer Satisfaction Total Company Effort The Marketing Concept Profit (or another Measure of long term Success) as an Objective Marketing Management Orientations Societal marketing concept is the idea that a company should make good marketing decisions by considering consumers’ wants, the company’s requirements, consumers’ long-term interests, and society’s long run interests. The societal marketing concept questions whether the pure marketing concept is adequate in • an age of environmental problems, • resource shortages • rapid population • worldwide economic problems • Neglected social services 1-23 Building Customer Relationships Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Customer relationship management is the overall process of building and maintaining profitable customer relationships by delivering superior value and Satisfaction Customer perceived value is the difference between total customer value and total customer cost Customer satisfaction is the extent to which a product’s perceived performance matches a buyer’s expectations 1-26 Companywide Strategic Planning Companywide Strategic Planning Strategic Planning Defining Strategy “The determination of the basic long-term goals and objectives of an enterprise and the adoption of courses of action and the allocation of resources necessary for carrying out these goals.” Alfred Chandler, Strategy and Structure, (MIT Press, 1962), Page 13. Strategic planning is the process of developing and maintaining a strategic fit between the organization’s goals and capabilities and its changing marketing Opportunities 2-4 Companywide Strategic Planning Strategic Planning Companywide Strategic Planning Types of Strategy Companywide Strategic Planning Defining a Market-Oriented Mission Strategic Vision : Concerns a firm’s future business path - “where we are going” . Mission statement: The organization’s purpose, what it wants to accomplish in the larger environment Market-oriented mission statement: Defines the business in terms of satisfying basic customer needs 2-5 Examples: Vision Slogans Levi Strauss & Company “We will clothe the world by marketing the most appealing and widely worn casual clothing in the world.” Nike “To bring innovation and inspiration to every athlete in the world. Greenpeace “To halt environmental abuse and promote environmental solutions.” Examples of Mission Statements Google “ To organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful” Blockbuster “To help people transform ordinary nights into BLOCKBUSTER nights by being the complete source of movies and games” Beacon Books “To inspire and equip business executives and entrepreneurs with essential information and knowledge they require for professional and personal growth” Companywide Strategic Planning: Defining Marketing’s Role Setting Company Objectives and Goals Business objectives The targets which appear in a business‘ profit and loss statement, including volume, revenue , gross margin and improve firm’s competitive position such as market share Marketing objectives The targets relating to the marketing deliverables/activities which enable a brand to achieve its business objectives (e.g. market share, consumer penetration, distribution coverage). Whenever possible, these should be set relative to competitors. 2-6 Companywide Strategic Planning: Defining Marketing’s Role Designing and Analyzing the Business Portfolio The business portfolio is the collection of businesses and products that make up the company Analyzing the current business portfolio is the process by which management evaluates the products and businesses making up the company 2-7 Companywide Strategic Planning: Defining Marketing’s Role Steps in Analyzing the Current Business Portfolio 1. Identify key businesses making up the company 2. Assess the attractiveness of its various SBUs 3. Decide how much support each SBU deserves 2-9 Companywide Strategic Planning: Defining Marketing’s Role Steps in Analyzing the Current Business Portfolio Identify key businesses making up the company • Strategic business unit (SBU) is a unit of the company that has a separate mission and objectives that can be planned separately from other company businesses • Company division • Product line within a division (Strategic Product Group) • Single product or brand 2-10 Companywide Strategic Planning: Defining Marketing’s Role Steps in Analyzing the Current Business Portfolio Assess the attractiveness of various SBUs and decide how much support each deserves 2-11 Companywide Strategic Planning: Defining Marketing’s Role Steps in Analyzing the Current Business Portfolio The Boston Consulting Group Growth – Share Matrix is a portfolio planning method that evaluates a company’s strategic business units in terms of their market growth rate and relative share Key Assumptions • Market growth has an adverse effect on cash flow because of the investment in such assets as manufacturing facilities, equipment and marketing needed to finance • Market share has a positive effect on cash flow as profits are related to Market Share The Boston Consulting Group Growth – Share Matrix 15% Stars Market Growth Rate Problem Children or Question Marks 7% Cash Cows Dogs 0 10 1 Relative Market Share 0 Companywide Strategic Planning: Marketing’s Role Defining Analyzing the Current Business Portfolio The Boston Group Approach Stars are high-growth, high-share businesses or products requiring heavy investment to finance rapid growth. They will eventually turn into cash cows. Cash cows are low-growth, high-share businesses or products that are established and successful SBUs requiring less investment to maintain market share Question marks are low-share business units in high-growth markets requiring a lot of cash to hold their share Dogs are low-growth, low-share businesses and products that may generate enough cash to maintain themselves but do not promise to be large sources of cash 2-13 Companywide Strategic Planning: Defining Marketing’s Role Analyzing the Current Business Portfolio Problems with Matrix Approaches • • • • Difficulty in defining SBUs and measuring market share and growth Time consuming Expensive Focus on current businesses, not future planning 2-15 Product Strategies for Growth : The Ansoff Matrix Products Existing Existing New Market Penetration or Expansion Product Development Market Development Diversification Markets New Companywide Strategic Planning: Defining Marketing’s Role Developing Strategies for Growth and Downsizing Product/market expansion grid is a tool for identifying company growth opportunities through market penetration, market development, product development, or diversification Product/market expansion grid strategies • Market penetration • Market development • Product development • Diversification 2-16 Product Strategies for Growth : The Ansoff Matrix Market Penetration is gaining/ winning competitors customers through buying competitors or more effective use of promotion, distribution or by cutting prices. Increase sales to current market segments without changing the product Market Expansion/Development: Growth strategy that identifies and develops new market segments for current products by converting non-users of it products. Lapsed users can also be targeted. You can also increase usage rate. Product Development option involves development of new or modified products for the existing markets. This can be done through product line extensions to give existing customers greater choice, product replacement e.g. car market where a new model replaces an old one, through innovation (replace of old with fundamentally different one) Market Development entails the promotion of new uses of existing products to new customers or marketing of existing products ( and their current uses) to new market segment Diversification : Growth strategy through starting up or acquiring businesses outside the company’s current products and markets Development of new products for new markets Marketing Management / Managing the Marketing Effort • Marketing Management is the process of planning, organizing, implementing and controlling marketing activities to facilitate exchanges effectively and efficiently. • Planning: is a systematic process of assessing opportunities and resources, determining marketing objectives and developing marketing strategy and plans for implementation and control • Organizing marketing activities involves developing the internal structure of the marketing unit. It can be organized by function, products, regions etc. • Proper Implementation of marketing plans hinges on coordination of marketing activities, motivation of marketing personnel, and effective communication within the unit. Marketing Management /Managing Marketing Effort Marketing Strategy Marketing strategy is the marketing logic by which the business unit hopes to achieve its marketing objectives Developing Strategy and Managing the marketing effort requires: • Analysis • Planning • Implementing • Controlling 2-24 Marketing Management/ Managing the Marketing Effort Marketing Analysis Analysis is the complete analysis of the company’s situation in a SWOT analysis that evaluates the company’s: • Strengths • Weaknesses • Opportunities • Threats 2-34 Marketing Management/ Managing the Marketing Effort Marketing Analysis Strengths include internal capabilities, resources, and positive situational factors that may help to serve company customers and achieve company objectives Weaknesses include internal limitations and negative situational factors that may interfere with company Performance Opportunities are favorable factors or trends in the external environment that the company may be able to exploit to its advantage Threats are unfavorable factors or trends that may present challenges to performance 2-35 Marketing Management/Managing the Marketing Effort Marketing Planning Planning is the development of strategic and marketing plans to achieve company objectives Marketing strategy consists of the specific strategies for target markets, positioning, the marketing mix, and marketing expenditure levels 2-37 Marketing Management/ Managing the Marketing Effort Marketing Planning : Strategy Market segmentation is the division of a market into distinct groups of buyers who have distinct needs, characteristics, or behavior and who might require separate products or marketing mixes Market segment is a group of consumers who respond in a similar way to a given set of marketing efforts. Target marketing is the process of evaluating each marketsegment’s attractiveness and selecting one or more segments to enter Market positioning is the arranging for a product to occupy a clear, distinctive, and desirable place relative to competing products in the 2-25 minds of the target consumer Marketing Management & Managing the Marketing Effort The Marketing Mix The marketing mix is the set of tools the firm uses to implement its marketing strategy. • The Marketing Mix is a term used to describe the combination of tactics used by a business to achieve its objectives by marketing its products or services effectively to a particular target customer group. • It is also referred to as the 4 Ps. i.e. Product, Price, Promotion and Place, or the 7 Ps the 4 Ps with the addition of People, Process and Physical Evidence. 2-28 Marketing Management and Managing the Marketing Effort Marketing Mix Product the need-satisfying offering of a firm. Marketing is about identifying, anticipating and satisfying Customer needs. You need to be sure that your products and services continue to meet your customers. needs. Place making goods and services available in the right quantities and locations when customers want them. Your choice will impact on your pricing and your promotion decisions. Price the amount of money that is charged for "something" of value Promotion communicating information between seller and potential buyer or others in the channel to influence attitudes and behavior. Marketing Management/ Managing the Marketing Effort Marketing Mix People The people employed in your organisation will determine the quality of service your customers receive. This is truer for services, but also impacts on businesses making tangible products. Happy, skilled and motivated staff make happy customers. Process The processes involved in delivering your products and services to the customer have an impact on the way in which your customers perceive you. Physical Evidence Physical evidence is a term used to describe the type of image that your business portrays through its physical presence, namely its premises, the appearance of its staff, its vehicles, etc. Marketing ManagementMarketing Management/ Managing the Marketing Effort & Managing the Marketing Marketing Implementation Implementing is the process that turns marketing plans into marketing actions to accomplish strategic marketing objectives Successful implementation depends on how well the company blends its people, organizational structure, decision and reward system, and company culture into a cohesive action plan that supports its strategies 2-39 Marketing Management/Managing the Marketing Effort • • • • Marketing Implementation Marketing Department Organization Functional Geographic Product Market or customer management 2-40 Marketing Management/ Managing the Marketing Effort Marketing Control Controlling is measuring and evaluating results and taking corrective action as needed Operating control involves checking ongoing performance against annual plan and taking corrective action as needed Strategic control involves looking at whether the company’s basic strategies are well matched to its opportunities Marketing audit is a comprehensive, systematic, independent, and periodic examination of a company’s environment, objectives, strategies, and activities to determine problem areas and opportunities 2-45 Measuring and Managing Return on Marketing Investment Return on Marketing Investment (ROI) Return on marketing investment (ROI) is the net return from a marketing investment divided by the costs of the marketing investment. Marketing ROI provides a measurement of the profits generated by investments in marketing activities. Customer-Centered Measures • Customer acquisition • Customer retention • Customer lifetime value 2-48 Marketing Strategy & Managing the Marketing Effort Marketing Planning • • • • • • • • Sections of a marketing plan include: Executive summary Current marketing situation Threats and opportunities Objective and issues Marketing Strategy : Target, Position, Marketing Mix Action programs Budgets Controls 2-38 The Role of Marketing Consumers • Provide consumers with goods and services that satisfy their needs, desires and expectations Firms • Attract Customers • Retain Customers Profitably • Efficient use of resources • Path to sustainable profitable growth • Key to competing in a liberalized market New and Growing Expectations of the Marketing Role in the Enterprise 1. 2. 3. 4. Insight Driven : Customer Champion Brand & Reputation Management Measurable and Accountable We will be pervasive, embedded across all channels to market 5. We will provide direction and vision and operate within an agreed strategic context 6. We will enable the sales process and drive growth The role of Marketing Society • Economic Growth and development through research and innovation • Value to Society : Competition drives down price and increases value to society • Higher Standard of Living: Products & Services that satisfy customers lead to employment and higher income Criticisms of Marketing • Marketing Encourages People to Purchase What is They Do Not Need • Marketers Embellish Product Claims • Marketing Discriminates in Customer Selection • Marketing Contributes to Environmental Waste • Marketing Encroaches on Customers’ Right to Privacy Marketing Activities • • • • • • • • • Marketing research Market analysis Setting strategy Planning Developing new products Managing product portfolios Managing and protecting brands Designing marketing channels Managing marketing channels • • • • • • • • Liaising with Agencies Recruiting and training staff Setting promotional objectives Designing promotional mix Analysing competitor activity Managing customer service Ensuring customers are satisfied Evaluating and reviewing activities and plans Marketing Management Framework Opportunities Impediments & Solutions Target Segment Corporate/ Business Objectives Marketing Objectives Sources of Volume/ Business Positioning Product Price Place Promotion Physical Ev. Process People Execute Evaluate New Capabilities in Marketing • • • • • • • Strategy and proposition development Through the line marketers Brand portfolio management Commercial Skills New media / digital Customer insight Data analytics