* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Double Aortic Arch
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Marfan syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Turner syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
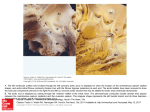
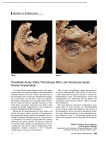
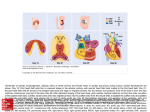
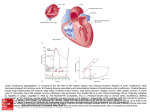
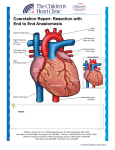
Double Aortic Arch What Is It? In this defect, the aorta, the large vessel that carries blood from the heart to the body, separates into two branches above the heart. This splitting occurs where the aorta begins its curve downward on its way to the lower body - known as the Aortic Arch. Normally, the Aortic Arch consists of a single vessel, from which minor arteries carry blood to the upper body. In this case, the Aortic Arch consists of two vessels, each of which has smaller arteries leaving it. The two branches of the Aortic Arch surround the esophagus (the tube which carries food to the stomach) and the trachea (the tube which carries air to and from the lungs). Before descending to the lower body, the two branches merge into one vessel, the Descending Aorta, as in a normal circulatory system. This rare defect, which is one of the so-called Vascular Ring anomalies, affects boys and girls equally. 1 Double Aortic Arch Normal Heart What Are Its Effects? The symptoms associated with this defect involve the constriction of the trachea (windpipe) and/or esophagus by the surrounding branches of the aorta. In the former case, breathing may be difficult as the trachea is compressed, resulting in wheezing or other respiratory distress. In the latter case, solid food may not be easily swallowed as the aortic branches narrow the esophagus, and vomiting or choking may occur. 2 Transparency applied to the left atrium and left ventricle, revealing the reconnecting aortic branches 3 How Is It Treated? This defect may take some time to be diagnosed as the symptoms are often mild. A Barium Swallow Study may be used to help identify the problem. If there is significant interference with breathing, surgery may be performed. Surgical treatment involves the tying off and separation of one of the branches of the Double Aortic Arch. Sometimes, one of the branches is already closed (atretic), with no blood flowing through it. In this case, it is simply clipped or tied off and separated from the other branch. In cases where blood flows through both branches, the smaller vessel is tied off and then severed at a point between the subclavian artery (SA in illustration) and where the smaller branch joins the larger branch to form the descending aorta. The ends of the remaining sections of the aorta are then closed with sutures (arrows in illustration). 4 Surgical Repair of Double Aortic Arch 5