* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How Do Soils Form? - Hicksville Public Schools
Entomopathogenic nematode wikipedia , lookup
Arbuscular mycorrhiza wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Agroecology wikipedia , lookup
Surface runoff wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Soil erosion wikipedia , lookup
Soil respiration wikipedia , lookup
Soil salinity control wikipedia , lookup
Terra preta wikipedia , lookup
Soil compaction (agriculture) wikipedia , lookup
Crop rotation wikipedia , lookup
Soil food web wikipedia , lookup
No-till farming wikipedia , lookup
Soil horizon wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Canadian system of soil classification wikipedia , lookup
Soil microbiology wikipedia , lookup
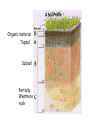
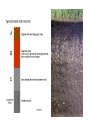
How Do Soils Form? Stop treating your soil like DIRT! Soil is a much more complex living thing than most people realize. All the mineral soil on earth today ultimately came from rocks created by ancient geologic forces. As this mineral soil is mixed with organic matter, bacteria, fungi and other soil organisms, it develops into a vibrant and very dynamic ecosystem with thousands (some say billions!) of different organisms. What is soil? • A mixture of weathered rock and organic remains that cover the bedrock of an area • The nature of the soil depends on the rocks from which the weathered material came, and the local climate Soil Horizons • The further weathering of soil produces distinct layers called horizons • Most soils of NYS do not exhibit the complete development of soil horizons Organic material Topsoil Subsoil Partially Weathered rock Horizons in a Soil Profile • Unweathered bedrock is the source of particles to make up soil • Partly weathered bedrock is the first stage towards soil formation Topsoil • Contains weathered rock and organic material • Humus is the term for organic material from decayed plants and animals • Also called Horizon A • Best layer for growing plants • Usually dark in color Subsoil • Below the topsoil • Also called Horizon B • When water passes through the topsoil, it leeches minerals and deposits them in the subsoil. • Subsoil is rich in in minerals but poor in organic material so it is not good for growing Transported Soils • Formed from weathered rock in another location and have been moved by an agent of erosion Residual Soil • Formed from the weathering of the bedrock that they overlie • Have the same mineral composition of the local bedrock Soil Conservation • Depletion may occur if the same crops are planted in soil year after year • Crop Rotation, contour plowing and strip cropping can prevent depletion Contour Plowing Strip Cropping Cross wind strip cropping laid out perpendicular to the prevailing wind direction.