* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Islamofascism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Somalia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Afghanistan wikipedia , lookup
Islamic ethics wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Spread of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Medieval Muslim Algeria wikipedia , lookup
Islamic socialism wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
Origin of Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
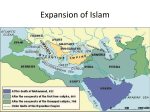
Rise of Islam and the First Empires The Life of Muhammad and the genesis of Islam ▪ Muhammad influenced the worship of a single, almighty god Allah ▪ Orphaned ▪ Resided in Mecca as a trader ▪ Married the widow Khadijah ▪ Revelations from Allah were given to Muhammad via the angel Gabriel in 610 CE ▪ Revelations were written in Arabic & collected in the Qur’an ▪ Basis for Islam ▪ Muhammed is seen as threat to the Umayyads ▪ Flees Mecca to Yathrib (Medina) on what is known as the Hijra (Ist year of Islamic Calendar) ▪ Quraysh launched a series of attacks on Muhammad and his followers in Medina Reasons for Islam in the Arab World ▪ Islam offered monotheism equal to that of Christianity & Judaism ▪ Also it was distinctively Arabic in origin ▪ Umma (Islamic community) offered political unity for tribal boundaries ▪ Bedouins united and conquered the Middle East ▪ Islam provided ethics ▪ Zakat – tax for charity ▪ Muhammad’s teachings & revelations in the Qur’an regulated ALL aspects of Muslim life ▪ Last Judgment The Arab empire of Umayyads Consolidation & Division in the Islamic Community ▪ There was a leadership crisis after Muhammad’s death ▪ Who should become the caliph? ▪ Abu Bakr ▪ Succeeded Muhammad as the 1st Caliph ▪ Ridda Wars ▪ defeat of rival prophets ▪ Restores unity of Islam Weakness of Adversary Empires A. Sassanid Empire Byzantine Empire ▪ Zoroastrianism ▪ Christian sects (Copts & ▪ Animistic religions ▪ Based on moral choices ▪ Muslims assassinated Sassanian rulers the ended the Sassanid empire in 651 Nestorians) rallied to Arab Muslims since they would tolerate Christians and tax them less heavily ▪ Copts & Nestorians viewed as heretics by Orthodox Byzantines ▪ The Byzantine empire survived Islam, but was constantly under siege by Muslim attacks Succession and the Sunni – Shiite split ▪ Uthman - 3rd caliph ▪ unpopular because he was chosen by the Umayyad ▪ Murdered by disobedient warriors ▪ Ali proclaimed caliph causing a split within Islam ▪ Ali ▪ Rejected by Umayyads as caliph ▪ Battle of Siffin ▪ Loses support because he tries to mediate with Umayyads ▪ Umayyad leader Mu’awiya proclaimed Caliph of Jerusalem & challenges Ali’s position ▪ Assassinated, 661 ▪ Ali’s Son, Hasan, ▪ renounces caliphate due to pressure from Umayyads ▪ Husayn (Ali’s other son) claims Caliphate ▪ Killed, Karbala, 680 Spread and Decline ▪ Umayyad Imperium ▪ Spread conquests into ▪ Central Asia ▪ Islam rivaled with Buddhism ▪ Northwest India ▪ North Africa ▪ Expansion into Europe blocked by Charles Martel and the Franks at Gibraltar ▪ Center of Islam shifts from Mecca to Damascus ▪ Alienation of Muslim faith led to revolts ▪ The Abbasid Revolt in Merv ▪ Supported by Shiites & Malwai ▪ Defeated Umayyads Early Abbasid Era ▪ Islam became a universal religion ▪ Sunni rule ▪ Suppressed Shiites who were seen as heretics ▪ Baghdad ▪ Capital of the Abbasid dynasty ▪ Bureaucratization of Islamic Empire ▪ Islamic Conversion & Mawali acceptance ▪ Integration of Arab & Non-Arab converts ▪ Most converted willingly Commercial Boom, Agrarian Expansion, and Social Standings ▪ Dhows – sailing vessels ▪ Traded with Christians and Jews ▪ Urbanization ▪ Government & private workshops ▪ Ayan – landowning elite ▪ Artisians were poorly paid ▪ Slaves did labor and unskilled work