* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download FN303-WSV
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Human digestive system wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
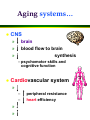
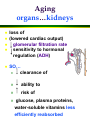
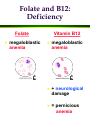
Nutrition and the Aging Adult The “graying of America” Physiological changes » nutritional implications Nutrients and aging » macronutrients, water » vitamins, minerals Nutrition and chronic disease Drug-nutrient interactions Lifestyle habits!! Trends in Aging Demographics/characteristics » age distribution in America » life expectancy » classification of the elderly – young-old = – old-old = – oldest-old = Societal implications Causes of death Ten Leading Causes of Death in the U.S. (2000) Rank Cause of death 1 Heart disease 2 Cancer 3 Stroke 4 Lung diseases 5 Accidents 6 Diabetes 7 Pneumonia/influenza 8 Alzheimer’s disease 9 Kidney disease 10 Septicemia Causes in which diet plays a part Causes in which alcohol plays a part Aging cells… Decreased cell division fewer parietel cells in stomach lining » absorption of Fe, Ca, Zn, vitamins B6, B12, folate efficiency of hormonal, enzymatic, neural communication Aging systems… CNS » » » brain blood flow to brain synthesis – psychomotor skills and cognitive function Cardiovascular system » – – » » peripheral resistance heart efficiency …GI tract senses of loss of sense of saliva, so ___________ can be difficult digestion of ______________ is generally normal nausea, diarrhea, constipation » anxiety » use of Aging organs…kidneys loss of (lowered cardiac output) glomerular filtration rate sensitivity to hormonal regulation (ADH) SO… » clearance of » ability to » risk of » glucose, plasma proteins, water-soluble vitamins less efficiently reabsorbed Aging… miscellaneous Lungs » decreased gas exchange Decreased ______________ adjustments » stress » temperature changes » glucose tolerance is slower Decreased Nutrients and Aging: Macronutrients Kcals: -7 to 10 kc/day per year over 18-19 » BMR, LBM (?) Protein » need ~1.0 g/kg BW to maintain _______________ » need adequate kcals to __________________ ___________ » 14 g/1000 kcal » for disease prevention ________: 1 ml/kcal » Increased risk of dehydration Nutrients and Aging: Vitamins Vit A: Vit D: ability to ____________ » osteomalacia Vit C: elderly men need more to maintain body pool Vit B6: RDA is increased to maintain ____________ Vit B12: ____% of elderly have decreased absorption » pernicious anemia Folacin: decreased _________ » UL set to prevent masking of vitamin ______ deficiency Terminology for pteroylglutamic acid Folic acid = term for synthetic form used in supplements and in food fortification Folate = term for naturally occurring form found in foods; generic term Folacin = generic term Tetrahydrofolate (THF) = active form Folate and B12: Functions Folate cell growth and division Vitamin B12 » DNA synthesis formation of heme formation of choline » involves homocysteine to methionine conversion homocysteine to methionine conversion » regenerates active THF synthesis of myelin sheath of nerves Folate and B12: homocysteine to met Conversion of homocysteine to methionine converts inactive THF to active THF, which is then converted to a form needed in DNA synthesis. active THF methionine nucleic acids vitamins B12, B6 homocysteine inactive THF DNA, RNA Folate and B12: Deficiency Folate megaloblastic anemia Vitamin B12 megaloblastic anemia + neurological damage = pernicious anemia SO… Why does megaloblastic anemia occur in a vitamin B12 deficiency? How can a vitamin B12 deficiency cause a folate deficiency? Which is a more serious deficiency--B12 or folate? Can you have a vitamin B12 deficiency without megaloblastic anemia? (The answer is “yes”; can you figure out why?) Would you want to have a vitamin B12 deficiency without megaloblastic anemia? (The answer is “no”; can you figure out why?) Why are the elderly at risk for B12 deficiency? absorption requires: » stomach acidity » Intrinsic Factor » special proteins from the stomach poor diet Sources of Folacin in U.S. Food Supply 1970 2% 18% 9% 20% Meat, poultry, fish 13% Dairy 28% 10% Grains Fruit 1994 Vegetables Legumes, nuts, soy Other 3% 12% 7% 20% 22% 24% 12% 1994: 331 mcg per capita available Folic acid fortification began January 1, 1998 Sources of Vitamin B12 in U.S. Food Supply Meat, poultry, fish Dairy Folate and B12: Supplements Dietary Folate Equivalents (DFEs) 1 DFE = 1 mcg food folate = 0.6 mcg synthetic folic acid in combination with food = 0.5 mcg synthetic folic acid taken on empty stomach Folic acid and B12 are the two supplements better absorbed in their synthetic forms DRIs for Vitamin B12 Life stage group Adults RDA (mcg/day) 2.4# #Since 10-30% of older people may malabsorb food-bound B12, it is advisable for those older than 50 years to meet their RDA mainly by taking foods fortified with B12 or a B12-containing supplement. Nutrients and Aging: Minerals ______: absorption decreased » after ________, women’s need also decreases Calcium » decreased ________ _________ deficiency » impaired _______ sensitivity _____ deficiency » » » taste acuity wound healing immune function Nutrients and Aging: Chronic Disease Osteoporosis » impaired __________ status » loss of __________ protection for bones so now bone is _________ faster than it is replaced Glucose tolerance » chromium status » overweight » low ___________ Heart disease Drug-Nutrient Interactions Drugs can interfere with nutrient intake, absorption, metabolism, excretion Nutrients can interfere with drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion Drugs can interfere with nutrients loss or stimulation of ________ digestion/absorption via: » HCl » chelation » competition for binding sites » damage to GI tract prevent ________ to active form antagonists affect ____ via metabolism and/or __________ _______ Nutrients can interfere with drugs influence _________ of absorption » chelation alter ________ via availability of plasma proteins » protein influence rate of _________ influence rate of _________ Drug-Nutrient Interactions Antagonism » vitamin __ vs. Coumadin » caffeine vs. tranquilizers Absorption problems » _______ and minerals » Al-antacids + _____ = absorption of Al » tetracycline and calcium » _________ and vitamin K Drug-Nutrient Interactions Nutrient losses » aspirin _______ » diuretics, laxatives Trigger ______ » MAO inhibitors + tyramine = Drug-Nutrient Interactions Side effects » digoxin, chemotherapy drugs » anticonvulsants increase need for __________ Nutrients as drugs » megadoses Drug-Nutrient Interactions Systemic effects of alcohol » tolerance decreases with age » depletion of __________ » poor nutrient intake » risk of _________ in diabetes