* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Design of 3.67 GHz RF Power Amplifier
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Scattering parameters wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Nominal impedance wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
History of the transistor wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
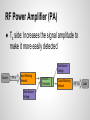
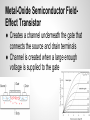
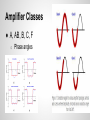
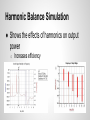
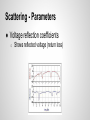
Design of 3.67 GHz RF Power Amplifier Presenters: Akshay Iyer, Logan Woodcock Advisers: Dr. K. Koh, Yahya Mortazavi Cognitive Radios ● Software defined radio ● Programmed to run by maximizing utility of radio frequency spectrum Project Goal Digital Baseband Processor Digital to Analog Converter Modulator Frequency Synthesizer (Oscillator) PA ● Design and simulate an RF power amplifier that operates between 2 and 4 GHz ● Use ADS software for design and simulation Antenna (Tx) Receiver (Rx) RF Power Amplifier (PA) ● Tx side: Increases the signal amplitude to make it more easily detected Gate Source Voltage Source RF In Input Matching Network Drain Source Voltage MOSFET Transistor Output Matching Network RF Out Load Metal-Oxide Semiconductor FieldEffect Transistor ● Creates a channel underneath the gate that connects the source and drain terminals ● Channel is created when a large enough voltage is supplied to the gate Smith Charts Used for Impedance Matching (Max Power Transfer) Transmission Line Theory Input Impedance Special Cases: Open/Short Circuit Stubs Amplifier Classes ● A, AB, B, C, F o Phase angles “Load Line” “Q - Point” - DC Operating Point DC+AC conditions: Vds=Vdd+Vac (time average of Vds must be Vdd) Vac=Vout Id=Iddc+Idac Idac=-Iload=-Vout/RL Final Schematic ● Consists of two bias networks, two impedance matching networks, and a MOSFET designed by Freescale. Transistor and Substrate ● Freescale Model MRF8S26060H ● Rogers Substrate Load Line / FET Curves Results ● Class AB o utilizes harmonics ● VDS of 50 V, VGS of 2 V Power Results ● Max Power Added Efficiency (PAE) of 88% Bias Networks ● Necessary to bias the transistor to desired level Load-Pull ● Shows impedance values specific to schematic Impedance Matching Networks 1. Shunt 2. Series Electrical Length (degrees) Harmonic Balance Simulation ● Shows the effects of harmonics on output power o Increases efficiency Scattering - Parameters ● Voltage reflection coefficients o Shows reflected voltage (return loss) Further Steps in the Process - Layout - EM simulation - Foundry mwrf.com References G. Saggio, Principles of analog electronics, Edition of book, Boca Raton: Taylor & Francis Group, 2014, p. . B. Razavi, RF microelectronics, 2nd ed., New Delhi: Dorling Kindersley India, 2012, p. 767-847.