* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ventricular Assist Devices: - Vanderbilt University Medical Center
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
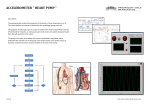
• These patients live in your community. Hospitalization $20.9 Total Cost $39.2 billion 53.3% 11.9% 6.4% 10.5% Lost Productivity/ Mortality* $4.1 Nursing Home $4.7 9.7% Home Healthcare $3.8 Physicians/Other Professionals $2.5 Drugs/Other Medical Durables $3.2 8.2% Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics— 2010 Update: A Report From the AHA Circulation, Feb 2010; 121: e46 - e215 • Ischemic cardiomyopathy • Non-ischemic cardiomyopathy New York Heart Association Functional Classification of Heart Failure Increasing Severity Class I Class II Class IIIa and IIIb Class IV • Cardiac disease • No symptoms • No limitation in ordinary physical activity • Mild symptoms (mild shortness of breath and/or angina) • Slight limitation during ordinary activity • Marked limitation in activity due to symptoms • Comfortable only at rest • Severe limitations • Symptoms even while at rest • Mostly bedbound patients Katz AM Heart Failure (Strength of Evidence = A) • ACE inhibitors • Beta Blockers • ARBs • Aldosterone Antagonists • Hydralazine and Isosorbide Dinitrate • Warfarin • In patients with atrial fibrillation, pulmonary embolism, or TIA • Loop Diuretics Lindenfeld, J, et al. J Card Failure 2010; 6, 486-491 Strength of Evidence = B Strength of Evidence = C • Antiplatelet agents (Aspirin) • Digoxin • Ischemic etiology of HF • Digoxin • In stage IV HF • Metalazone • In stage II and III HF • Thiazide diuretics • Warfarin • MI patients with LV thrombus Lindenfeld, J, et al. J Card Failure 2010; 6, 486-491 Inotropes • Commonly used on an outpatient basis for stage IIIb – IV heart failure • Milrinone and Dobutamine are the only FDA approved drugs for outpatient use • Not recommended for acute heart failure exacerbations in ischemic patients • Probable benefit in non-ischemic exacerbations • OPTIME-CHF JAMA 2002; 287:1541-7 Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) • LVEF <35% • NYHA class III – IV • QRS > 120 ms • Optimal medical therapy Implantable Cardiac Defibrillators • Ischemic Etiology • (Strength of Evidence = A) • Non-ischemic Etiology • (Strength of Evidence = B) • Primary prevention of ventricular arrhythmias • LVEF <35% Lindenfeld, J, et al. J Card Failure 2010; 6, 486-491 Decreased end organ perfusion • Renal function • Liver function • Pulmonary function We need more support! A mechanical circulatory device used to partially or completely replace the function of either the left ventricle (LVAD); the right ventricle (RVAD); or both ventricles (BiVAD) Long-Term LVAD Short-Term LVAD ANY • Are there any contraindications to VAD support? • • • • • • End-stage lung, liver, or renal disease Metastatic disease Medical non-adherence or active drug addiction Active infectious disease Inability to tolerate systemic anticoagulation (recent CVA, GI bleed, etc.,) Moderate to severe RV dysfunction for some LVADs • What are our other issues in this particular patient? • What are the patient’s goals? What are our goals? • What happens if we don’t meet our goals? INTERMACS SCORE Interagency Registry for Mechanically Assisted Circulatory Support Long-Term LVAD Ideal candidates are INTERMACS classes 3-4 Short-Term LVAD Candidates are INTERMACS classes 1-2 Not a LVAD Candidate INTERMACS 1 or those with multisystem organ failure Lietz and Miller Curr Opin Cardiol 2009, 24:246–251 Long-term placement Bridge to Transplantation (BTT) • • • Patient is approved and currently listed for transplant NYHA IV Failed maximized medical therapy Destination Therapy (DT) • • • • • • http://www.cms.gov/medicarecoverage-database Not a heart transplant candidate NYHA IV LVEF <25% Maximized medical therapy >45 of 60 days; IABP for 7 days; OR 14 days Functional limitation with a peak oxygen consumption of less than or equal to 14 ml/kg/min Life expectancy < 2 years Bridge to Transplantation (BTT) Destination Therapy (DT) HeartMate II (Thoratec) Pump Speed (RPM) – How quickly the pump rotates Pump Power (Watts) – Measure of motor voltage and current Pump Flow (L/min) - Estimated value of the volume running through the pump Pulsitility Index – The measure of the left ventricular pressure during systole VS Outflow graft (kink , leak) Inflow cannula (poor position, obstruction) Drive line infection / fracture Pump/rotor dysfunction (thrombus) Controller malfunction Battery dysfunction Winston Churchill Rose, EA; et al NEJM 2001; 345:1435-1443 Kirkland, JK, et. al JHLT 2013; 32:141-156 Kirkland, JK, et. al JHLT 2013; 32:141-156 • Shock Team Evaluation for mechanical circulatory support (MCS) • Try to avoid the bridge to decision or the bridge to nowhere • Utilized for LV support only; not appropriate to use with RV failure • Impella 2.5 can be inserted through the femoral artery during a standard catheterization procedure; provides up to 2.5 L of flow • Impella 5.0 inserted via femoral or axillary artery cut down; provides up to 5L of flow • The catheter is advanced through the ascending aorta into the left ventricle • Pulls blood from an inlet near the tip of the catheter and expels blood into the ascending aorta • FDA approved for support of up to 6 hours • Used for LV support; not appropriate in RV failure • Cannulas are inserted percutaneously through the femoral vein and advanced across the intraatrial septum into the left atrium • The pump withdraws oxygenated blood from the left atrium and returns it to the femoral arteries via arterial cannulas • Provides up to 5L/min of flow • Can be used for up to 14 days • Can be used for LV and/or RV support • Cannula are typically inserted via a midline sternotomy • Capable of delivering flows up to 9.9 L/min • Can be used for up to 30 days • Used for patients with a combination of acute cardiac and respiratory failure • A cannula takes deoxygenated blood from a central vein or the right atrium, pumps it past the oxygenator, and then returns the oxygenated blood, under pressure, to the arterial side of the circulation • Can be used for days to weeks