* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Digestive System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
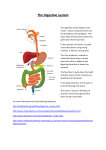
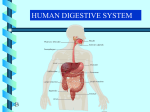
Digestive System 1. What are the main functions of the digestive system? To break down food into molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and passed to the cells for use. 2. The digestive tract can also be referred to as? The alimentary canal. 3. The teeth and tongue begin to break down food. Is this mechanical or chemical? 4. Which fluid is used to lubricate the passage of food down the throat? Saliva 5. What name is used for the wave-like motion which transports substances in the digestive tube? peristalsis 6. Name the main acid in our stomach. HCL – hydrochloric acid 7. What is chyme? The mixture of food, water, and enzymes found in the stomach and small intestine 8. Where is the pylorus sphincter located? At the bottom of the stomach, leading to the small intestine. 9. What occurs in the colon? Absorption of water and packing of solid waste 10. Which organs are identified as secreting digestive juices into the digestive tract? Stomach, Liver, and Pancreas 11. Which cartilage structure ensures that food enters the esophagus, not the larynx? Epiglottis 12. What is heartburn? The relaxation of the gastro-esophageal sphincter at the top of the stomach allowing stomach acids to rise into the esophagus. 13. Name the three salivary glands. Sublingual, submandibular, parotid 14. Which events are mentioned that stimulate the salivary glands? Food in the mouth, sight or smell of food, irritation of lower GI tract by bacteria or virus. 15. What are the mumps? Viral infection of parotid glands 16. What prevents the stomach from digesting itself? Mucous coating./ Also, what term is used for a break in the stomach lining? ulcer 17. Which sphincter serves as a valve between the stomach and small intestine? Pyloric sphincter 18. What is the small intestine responsible for? Absorption of nutrients 19. Describe each of the following: Duodenum: first section, fairly immoveable, curves around head of pancreas, ducts delivering bile and pancreatic juice empty in here; ilium: last section of small intestine, joins large intestine at iliocecal valve: jejunum: middle section of small intestine 20. Describe where it is located. See above 21. What is the inflammation of the appendix? A bacterial infection of the vermiform appendix located off of the cecum of the large intestine. 22. What is the main function of the large intestine? To absorb water and pack waste 23. Put the eight sections of the large intestine in order starting with cecum and ending with the anus. Ascending colon, right colic flexure, transverse colon, left colic flexure, descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum, anal canal 24. Functions of the liver. The liver makes bile, stores glycogen, stores fat-soluble vitamins A,E,D, and K, acts as a detoxifiying system for alcohol and drugs 25. Size of the liver. Liver is the largest gland of the body, weighing about 3 pounds. 26. Enzymes produced by the liver are introduced into? Gall bladder 27. Function of the gall bladder? To store bile, which emulsifies fats 28. Describe the color and location of the gallbladder? On the underside of right liver lobe, has a greenish tint 29. Through which vessel does the gall bladder send bile to the duodenum? Common Bile Duct 30. Which condition results from the crystallization of bile components? Gall stones 31. Function of the pancreas? Primary enzyme producer for the digestive tract, secretes pancreatic juice that that contains a broad spectrum of enzymes 32. Describe the size and location of the gland. Soft, pink, triangular gland, extends across abdomen from the spleen to close to the duodenum, and lies behind the greater curve of the stomach. 33. Which hormone regulates the synthesis of HCl acid in the stomach? Gastrin 34. Secretion of saliva is under the control of which system? ANS - Parasympathetic 35. What is the frenulum? A fold of tissue that hold tongue to the floor of the mouth 36. What are the four divided parts of the stomach and description of each?Cardia region – where food enters the stomach; Fundus – expanded part of stomach that bluges superolaterally to the cardia; Body – mid-portion of stomach; pylorus – terminus of stomach, is continuous with the duodenum through the pyloric sphincter 37. List and describe the 4 layers of the GI tract from the outer most to the inner most? Mucosa – moist epithelial membrane that lines the cavity; Submucosa – areolar connective tissue just deep to the mucosa; Muscularis – smooth muscle to propel food; Serosa – the visceral peritoneum, or outer edge of the alimentary canal 38. Which is longer in length, the small intestine or large intestine? Small intestine 39. Which is larger in diameter, the small intestine or large intestine? Large intestine 40. Know the symptoms of: gastritis (an inflammation of stomach wall, can cause gastric ulcers), hepatitis (inflammation of liver, causes jaundice and poor cleansing of blood), hernia (tear in muscle wall allowing internal organs to protrude through, causes pain, vomiting (abrupt removal of chyme from the stomach via the gastroesophageal sphincter. 41. “Disassembly line” notes Nutrition 42. Correct order of macromolecules to leave stomach: Carbohydrates, proteins, fats 43. Order of abundance in body: Proteins, Fats, Carbs 44. Carbohydrates which form is most useful? Monosaccharides What do necessary item do carbs supply? Glucose to make ATP RDA - 58% of daily intake 45. Fats Highest potential energy per gram 9calories per gram Used for? Stored for use as an energy source, used to make cell membranes, help body absorp fatsoluble vitamins RDA 30% of daily intake 46. Proteins Major supplier for body tissues, structures, and processes Used for? To build tissues, to make enzymes for body processes RDA: 12% of daily intake What are the building blocks of proteins? Amino acids 47. Vitamins What kind of compound? organic What do vitamins assist with in the body? Help body to use nutrients 48. Calories Know which foods yield how many calories (kilocalories) Carbs 4, fats 9, proteins 4 Know basic digestions rates for different macromolecules 49. Disturbed eating habits: strict dietary rules, restricted food intake, altered mealtime behaviors 50. Men and eating disoders: 10% of ED diagnosis are in men 51. Starvation syndrome: blackouts, loss of concentration, irritability, muscle weakness 52. Amenorrhoea – cessation of a woman’s monthly menstruation 53. Purging: normally only 30% of the calories consumed are purged through vomiting 54. Essential fats: fats are necessary for cell membranes, steroid hormones, and synthesizing certain vitamins 55. Omega-3 fats aid in reducing triglycerides, preventing blood clot formation, reducing high blood pressure and regulating heart rhythm 56. 35% of American adults are obese 57. Waist measurement (over 35” for women and over 40” for men) is correlated with heart disease and Type 2 diabetes 58. In America, 80% of all gallstones are cholesterol; 20% are pigment based Diagrams: Digestive System (Alimentary Canal and Accessory Organs) Stomach