* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Essay Question Outline
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
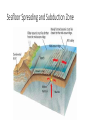
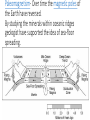
Essay Question Outline (any blue Underline words are links please click on them to discover or review) 1. Plate Tectonics 2. Continental Drift 3. Subduction 4. Isostasy 5. Sea Floor Spreading 6. Paleomagnetism Alfred Wegener: The Theory of Plate Tectonics a. Continental Drift • Started: All land was joined into 1 supercontinent called “Pangaea: • Over Time: Continents drifted apart creating Gondwanaland and Laurasia, then Laurasia broke apart into North America, Europe and Asia. Then Gondwanaland broke into Africa, South America, Antarctica and Australia. Then India collided with Eurasia. Continents continue to drift apart due to the convection currents in the Earth to where the continents are today. • Future: The plates will continue to move based on if they are divergent (away), convergent (towards) or transform (slide) boundaries until the all come back together with an inland sea in the middle creating Pangaea Ultima Alfred Wegener: Evidence • Animal and Plant Fossil • Mesosaurus – S. Am and Africa both had fossils but couldn’t swim in fresh water so the continents had to be connected • Landforms Created: • Himalayan Mountains when India and Eurasia collided • Fit together like a puzzle • Coast of South America and Africa Alfred Wegener: Evidence continued • Features common to southern continents: • rock types and ages (Geochronology Map) • Glaciation of late Paleozoic age • Convection Currents • Hot spots don’t move but the islands due • Subduction Zones • Seafloor spreading • Paleomagnetism • Earth’s Magnetic Field switched Subduction Zone = Isostasy Happens • Subduction: Two plates “converge” together. One plate is forced UNDER the other and into the Mantle. • Oceanic Plate more Dense so slips under Continent Plate less dense creating a trench, volcanoes, island arc • Trench: An underwater canyon indicating a subduction zone and convergent plate boundaries. Isostasy • The earth’s crust can move up and down as a result of the interaction of the downward force of the crust and the upward force of the mantle. The balance between these two forces is called isostasy. • Examples: Boats, rubber ducks, log float in the water, glaciers/icebergs, Earth’s crust on the mantle, subduction zones. Seafloor Spreading • Sea-floor spreading is the process in which the ocean floor is extended when two plates move apart (divergent boundaries) • Mid Atlantic Ridge • Tectonic plates move away from each other making a crack along the ocean floor. • Molten Rock rushes upward through the crack and is solidified by the cooler water. • This process creates new rock and fills in the crack. (oceanic ridges) • The ocean floor spreads as a result. Seafloor Spreading and Subduction Zone Paleomagnetism- Over time the magnetic poles of the Earth have reversed. By studying the minerals within oceanic ridges geologist have supported the idea of sea-floor spreading. Hot Spots Mantle plumes are areas of hot, upwelling mantle. A hot spot develops above the plume. Magma generated by the hot spot rises through the rigid plates of the lithosphere and produces active volcanoes at the Earth's surface. As oceanic volcanoes move away from the hot spot, they cool and subside, producing older islands, atolls, and seamounts. As continental volcanoes move away from the hot spot, they cool, subside, and become extinct. Hawaii Hot Spots • Hawaii is the youngest island and it is still being formed today; thus, Hawaii is currently at the hot spot location.