* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Disordered Eating
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
Impulsivity wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Munchausen by Internet wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Conduct disorder wikipedia , lookup
Addictive personality wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Substance use disorder wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Obsessive–compulsive personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
History of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Rumination syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Externalizing disorders wikipedia , lookup
Anorexia nervosa wikipedia , lookup
Bulimia nervosa wikipedia , lookup
Eating disorders and memory wikipedia , lookup
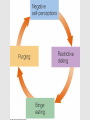
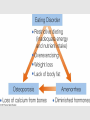
Disordered Eating Disordered Eating vs. Eating Disorder • Eating disorders are psychiatric conditions – Extreme, continuous body dissatisfaction coupled with long-term eating patterns that negatively affect body functioning – Typical behaviors = food restriction, obsessive exercise, self-induced vomiting – Anorexia & bulimia nervosa Disordered Eating vs. Eating Disorder • Disordered Eating general application of atypical eating behavior to maintain low weight – Going on & off diets; refusing to ingest fats – Usually not chronic behaviors: rarely cause illness – Many people do seek psychiatric care for it Intimately tied to body image • Body image: the way you feel about your body Factors contributing to Eating Disorders • • • • • Family environment Unrealistic media images Sociocultural values Personality traits Genetic & Biological factors Factors contributing to Eating Disorders • Family environment – You’re more likely to develop an eating disorder if a sibling has one – Families with anorexic member are more “uptight” • Rigid structure; avoidance of controversial topics; fuzzy interpersonal boundaries – Families with bulimic member are more “chaotic” • Less stable organization; less nurturing; more angry & disruptive Factors contributing to Eating Disorders • Unrealistic media images – Adolescents are less capable of understanding that these are uncommon, unrealistic, and often unnatural body types. – Consequently less able to distance themselves from a need to acquire that body Factors contributing to Eating Disorders • Sociocultural values – “Western values” contribute to eating disorders • Significantly more common in white Western women than others (worldwide) – Everyday interactions with family and peers influence how we feel about our bodies Factors contributing to Eating Disorders • Personality Traits – People with anorexia nervosa tend toward social inhibition, compliance, emotional restraint • Do these traits predispose one to the disease, or are they side-effects of starvation? – People with bulimia nervosa tend to be impulsive, extroverted, have low self-esteem • • • • seek external validation Prone to mood swings that result in binging Prone to self-criticism Prone to anxiety disorders and substance abuse Factors contributing to Eating Disorders • Genetic & Biological factors – Both bulimia & anorexia are much more common among related individuals • Could be due to genetic or cultural transmission – Twin studies of bulimia nervosa found that relatedness (heritability) & key environmental factors EACH accounted for ~50% of the variability in who was diagnosed – Imbalances in hormones involved with feelings of hunger may also be involved Anorexia nervosa • Suite of unhealthful practices employed to reduce weight below 85% of normal (for height & weight) • 90-95% are young women • 0.5-1% of US females develop AN – 5 - 20 % of those diagnosed will die from complications within 10 years. • Leading cause of death in females aged 15-24 Anorexia nervosa • Symptoms: – Self-starvation; refusal to maintain minimal body weight – Intense fear of weight gain, despite being underweight by all measures – Undue influence of body weight on selfimage or denial of problem – Amenorrhea in women past puberty • Absence of at least three menstrual cycles Anorexia nervosa • Health risks: – Loss of body fat – Loss of proteins from skeletal muscle and organs. Reduction of non-vital functions • Periods cease; growth stops – Electrolyte imbalance - leads to irregular heart beat & heart failure (cramping is least of your worries) – Cardiovascular problems - tachycardia, low bp, dizziness – GI problems - general weakness & loss of function – Osteoporosis…why? Bulimia nervosa • Binging – High rate & quantity of food consumption: more than usual (in relation of time, place, social context) – Loss of self control; inability to stop; sense of euphoria – Occur ~ twice or more per week • Purging – Usually, but not always, after each binge – Vomiting, laxatives, obsessive exercise Bulimia nervosa • Prevalence – Affects 1-4% of women (estimate) – Mortality rates much lower than for AN (1% dying within 10 years) – Occurs mostly in women, but also in men competing in sports requiring a thin build Bulimia nervosa • Symptoms – Recurrent episodes of binging – Recurrent inappropriate compensatory behavior (laxatives, vomiting, diuretics) – Binge-purge cycle continues for more than three months – Body shape & weight unduly influence selfimage Bulimia nervosa • Health risks – Electrolyte imbalance leads to irregular heart beat & heart failure • Caused by dehydration & loss of Na+ and K+ through vomiting – GI problems: inflammation, ulceration, possible rupture of esophagus • Caused by HCl + mechanical trauma from frequent vomiting – Dental problem: tooth decay, staining & mouth sores • HCl in vomit – Calluses on hands, swelling in cheek & jaw area Disordered Eating patterns • Binge eating • Chronic dieting • Chronic overeating Binge Eating Disorder • Symptoms: – Often overweight – Lack of control during binging – Chaotic eating behaviors (eating too fast, too much, in private) – Negative self-esteem, poor body image – Often associated with depression, substance abuse, anxiety disorders Binge Eating Disorder • Health Risks: – Increased risk of overweight or obesity – Foods eaten during binge are often high in fat and sugar – Increased stress (caused be negative selftalk) leads to psychological distress Chronic Dieting • Symptoms: – Preoccupation with food, weight, calories • Classify food as “good” or “bad” – Strict dieting – Excessive exercise • Chronic fatigue – Loss of concentration; mood swings – Increased criticism of body shape Chronic dieting • Health Risks: – Insuffiecient nutrient intake – Insufficient caloric intake • low vitamin and mineral intake – Decreased energy expenditure due to a reduced BMR – Decreased ability to exercise – Increased risk of eating disorder Reduced BMR with dieting Female Athlete Triad • Female athlete triad: serious medical syndrome frequently seen in female athletes; consists of – Disordered eating – Menstrual dysfunction – Osteoporosis • Seen especially in sports that emphasize lean bodies or use subjective scoring – Examples?