* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Rise and Fall of the Caliphates
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Imamah (Shia) wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Spread of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Muhammad and the Bible wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
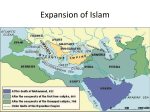
The Rise and Fall of the Caliphates Chapter 8 (p. 202 - 208) Muhammad’s Successors Spread Islam In 632, Abu-Bakr became the first caliph (“successor”) Abu-Bakr & next 3 caliphs (Umar, Uthman & Ali) had known Muhammad Used Qur’an & Muhammad’s actions as guide to leadership Known as “rightly guided” caliphs Rule known as the caliphate Muhammad’s Successors Spread Islam After Muhammad’s death, some tribes on Arabian peninsula broke away from Islam & refused to pay taxes Abu-Bark invoked jihad (“striving”) Armed struggle against non-believers Abu-Bakr used jihad to expand Islam After Abu-Bakr died (634), Umar expanded Muslim state to include Syria, Lower Egypt & part of Byzantine Empire By 750, Muslim Empire stretched from Atlantic Ocean to Indus River Muhammad’s Successors Spread Islam Muslims allowed conquered people to worship their own religion Christians & Jews received special treatment Still had to pay taxes & subject to various restrictions Couldn’t spread religion, but could be officials, scholars, bureaucrats, etc. Internal Conflict Creates a Crisis 656, Uthman murdered & Ali (Muhammad’s cousin & son-in-law) was chosen as natural successor Ali’s rule was challenged by Muawiya (governor of Syria) 661, Ali assassinated Umayyad (led by Muawiya’s son) come to power & move capital to Damascus Arabs upset that capital was so far away Began to live a life of luxury Internal Conflict Creates a Crisis Majority of Muslims accepted Umayyad rule (to maintain peace) Shi’a (party of Ali) resisted Umayyad rule Believed caliph needed to be descendent of Muhammad Viewed position of caliph as secular, not religious Known as Shi’ites Sunni (followers of Muhammad’s example) did not outwardly resist Umayyad rule Didn’t look to a single authority to define true belief Sufi rejected luxurious life of Umayyad and vowed to live a life of poverty Rebel groups overthrew Umayyad in 750 Abbasids (most powerful of rebels) took control Control Extends Over Three Continents Abbasids murdered remaining Umayyad family Prince Abd al-Rahman escaped to Spain & set up Spanish Umayyad caliphate Muslims in Spain known as Berbers Muslim state in Spain called al-Andalus Abbasids move capital to Baghdad (central Iraq) to consolidate power Experienced “Golden Age” in which main currents of theology & law were founded (based on Greek philosophies by Aristotle) Control Extends Over Three Continents Abbasid caliphate lasted from 750 - 1258 Abbasids increased power but failed to keep complete political power over empire As Islam conversion accelerated, the empire became difficult to control Independent Muslim states sprang up Decreased the prosperity of Baghdad Abbasids hired mamluks (Turkish slaves) to protect themselves from their own distrusted generals & troops in outlying areas Couldn’t afford to pay them, so mamluks overran Abbasid empire from 835 - 892 & moved capital to Samarra Fatimid = caliphate formed by Shi’ites who claimed to be descendents ot Muhammad’s daughter Fatima Governed out of Cairo Political fragmentation led to strained food resources Internal quarrels occurred during the Crusades Finally, Mongol invasions destroyed Baghdad ending the Abbasid caliphate in 1258