* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Great War Notes
Australian contribution to the Allied Intervention in Russia 1918–1919 wikipedia , lookup
Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
History of Germany during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of World War I wikipedia , lookup
American entry into World War I wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk wikipedia , lookup
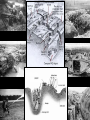
The Great War Developing Conflicts • Militarism – Building and maintaining a powerful military – Fascination with the glory of war – Caused an arms race • World powers competed to have the best • Goal was to have greatest and most technologically-advanced armies and navies • Can be viewed as an aggressive move toward war • Fostered mistrust, especially between enemies – Focus on mobilization • Prepared for immediate organization for war – Source of pride for people for their country Developing Conflicts • Nationalism – Strong feelings of pride and unity among people of a nation – Devotion to one’s nation – Created competition among nations • Race for territory to build empires • Spurred rivalries – Balkan Peninsula • Small ethnic groups demanded independence from larger empires like Austria-Hungary and Russia Developing Conflicts • Imperialism – Building empires by expanding territory to gain colonies – Increased competition between world powers • Early disputes were settled to avoid war – Deepened rivalry and mistrust between world powers – Increased nationalism in citizens – Fueled industry Developing Conflicts • Alliances – Agreements between countries to help each other in wartime – Triple Entente • France • Britain • Russia – Triple Alliance • Germany • Austria-Hungary • Italy – Other agreements made as well, including aid for weaker nations (Russia and Serbia) Balkan Crisis • Area of southeast Europe in conflict • Many small ethnic groups want independence • Serbia and Austria-Hungary clashed over territory of Bosnia • A-H annexed Bosnia in 1908, angering Serbia • Tensions rose into 1914 • Archduke Franz Ferdinand and his wife Sophie appeared in Sarajevo, capital of Bosnia – Heir to A-H throne • Assassinated by a Serbian nationalist • A-H declares war on Serbia • Pre-war alliances activated = WAR Tangled Alliances • Wartime Alliances: – Central Powers • Germany • Austria-Hungary • Italy (until 1915) – Allies • • • • • Great Britain France Russia Japan Italy (1915) Sequence of Events • 1914 – Assassination of Archduke by Serbian nationalist – Austria-Hungary declares war on Serbia – Russia comes to aid of Serbia – Germany declares war on Russia – France declares war on Germany – Germany invades Belgium and France – Great Britain declares war on Germany *America declares neutrality Fronts of Fighting • Western Front – France vs. Germany • Eastern Front – Russia vs. Germany • Italian Front – Italy vs. AustriaHungary Total War • Trench Warfare – New weaponry introduced • Long-range artillery • Poisonous gases • Gas masks • Tanks • Machine guns • Flame throwers *submarines • Trenches – Used to protect soldiers – Parallel lines of fighting – Heavy loss of life – Little land gains – Miserable conditions • No sleep, little food • Rats, dead bodies • Fueled by industrial power • Weapons and soldiers were quickly replaced early on • By 1915, stalemate existed at all fronts Sequence of Events • 1917 – Russia withdraws from the war – United States enters the war Russian Revolution • Before the Revolution: – Most Russians were poor and many were starving – Russia had lost millions of lives to the Eastern front of fighting • The Revolution: – Czar Nicholas II (the last emperor of Russia) was forced by the Russian people to give up his throne • He wanted to keep fighting in WWI • He ignored the demands for change from peasants and workers – Civil War • The Bolsheviks (Communists), led by Vladimir Lenin, defeated their enemies and took control of Russia – Russia withdrew from WWI – Russia was transformed into a communist nation and was renamed the Soviet Union (a.k.a. the U.S.S.R.) America Enters The Great War • In the beginning, America declared neutrality • Reasons for U.S. entry into the war: – Economic relationships with the Allies • The U.S. had been selling many products and loaning a lot of money to the Allies and (privately) wanted them to win the war – Unrestricted submarine warfare • To prevent supplies from getting to the Allies, German U-boats sunk boats without warning – Sinking of the Lusitania – 128 Americans killed! America Enters The Great War • The Zimmermann Telegram – A note from the German government asking Mexico to attack the U.S. was intercepted and published in newspapers • Arrival of fresh US troops helped the Allies win war Sequence of Events • 1917 – Russia withdraws from the war – United States enters the war • 1918 – Germany agrees to armistice (Nov. 11 at 11am) – President Wilson’s Fourteen Points Speech – Paris Peace Talks – Treaty of Versailles signed Armistice • Germany accepted the cease-fire in 1918 • Paris Peace Talks – “The Big Four” met to discuss terms of peace • Great Britain – Wanted to protect colonies – Wanted harsh punishment for Germany • France – Wanted to protect colonies – Wanted harsh punishment for Germany • Italy – Wanted colonies it was promised • United States – President Wilson’s Fourteen Points American Peace Plan • President Wilson’s Fourteen Points Plan – Addressed the causes of the war to bring peace – Proposals that would reduce problems caused by excessive nationalism, imperialism, alliances, and militarism – Created a League of Nations • Organization with member nations that maintained global peace – For others, it wasn’t harsh enough Treaty of Versailles • Other Allies wanted harsh consequences for Germany • Final Peace Treaty: – Germany must pay war reparations (put Germany in debt) – “War Guilt Clause” forced them to accept blame for the war – Restrictions on Germany military’s size and ability – Demilitarization of Rhineland (territory near France) – German territorial losses – League of Nations League of Nations • Organization of member nations that work together to keep global peace • Ineffective, weak, lacked power • No authority over nonmembers – United States didn’t join – Germany and Soviet Union not allowed – Italy and Japan withdrew • No way to enforce peace – Member nations had to send military – Many were reluctant after such a brutal war • Required unanimous consent for decisions