* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bones and ligaments
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
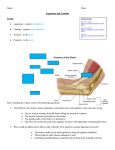
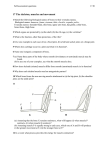
Organization • Cell (ex=muscle cell) • Tissues (many of the same types of cells ex muscle tissue) • Organ (many tissues that work together ex heart) • Organ system level (many organs work together ex circulatory system) • Organism level (many organ systems work together) Bones and ligaments Bone Structure • Compact bone – hard outer surface • Spongy bone – Swiss cheese like matrix interior. To cushion impact. • Bone marrow – source of red and white blood cells • Haversian Canals – blood vessel canals through compact bone osteoporosis • Disease of the bone, causes of which are largely unknown. – Mineral deficiencies promote disease, especially Calcium. – Decrease in bone density – Predominantly older women – Prevention – Get plenty of Calcium at a young age, exercise helps build bone strength Joints – 4 types • Ball and socket – all directions – Shoulder and hips • Pivot joints – twist around – Arm, vertebrae • Hinge joints – lever or hinge action – knees, fingers, toes • Gliding – slide past one another – Wrist, ankle Ligaments • TOUGH connective tissue that links bones to bones Ligaments • Connect bone to bone (joints) Tendons • Collagen connective tissue that links bone to muscle. When muscle contracts, pulls on tendon, moves bone. Muscles and Muscular Contraction 3 types of muscle cells • Smooth muscle – internal organ walls, blood vessels (enables dilation and contraction) – Sheets of cells, all acting in concert – Many work together to squeeze – Involuntary muscle • Cardiac Muscle – Only found in heart – Striated – Involuntary – group of cells contract together • Skeletal Muscle •Voluntary muscle • Multinucleated •Striated •The muscles in your arms, legs, etc. Skeletal cont… • Structure: MuscleFasicle Myofiber (cell) Myofibril (with many sarcomeres)Myofilaments • Many myofibers connected lengthwise through entire fiber • Many mitochondria • Many nuclei (why? The multiple nuclei arise from the fact that each muscle fiber develops from the fusion of many cells (called myoblasts). Skeletal cont… • Sarcomere (small part of myofibril) – Made up of thin (Actin) and thick (Myosin) filaments – Thin slide across thick Contraction – Sliding Filament Theory • When muscle contracts its shortens. When muscle relaxes it DOES NOT lengthen beyond relaxed state • Actin and Myosin slide across one another (they do not shorten or lengthen) • Myosin head binds actin and pulls it, causing sliding. Requires help of Calcium ATP and _______. Actin/Myosin animation