* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide ()
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
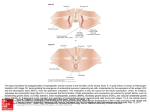
Possible mechanisms by which overloading can cause progressive deterioration of the heart (cardiomyopathy of overload). Several mechanisms, including myocyte stretch, activate a growth response that initiates myocardial hypertrophy in the overloaded heart (left). The same growth response can also activate signal transduction systems that cause programmed cell death (apoptosis). The hypertrophic response to overload, by causing sarcomeres to be added in series, can also lead to cell elongation and accelerate remodeling; the resulting increase in wall tension, together with the overload itself (right), increases cardiac energy expenditure that, in the overloaded heart, can accelerate myocyte necrosis. Reduced cardiac output activates neurohumoral responses (center), which, by increasing afterload and β–adrenergic stimulation of the heart, also increase cardiac energy expenditure. Because many Source: Chapter 26. Pathophysiology of Heart Failure, Hurst's The Heart, 13e mediators of the neurohumoral response to a decrease in cardiac output promote myocardial cell growth, neurohumoral activation can also accelerate both Citation: Fuster V, Walsh RA, Harrington RA. Hurst's The Heart, 13e; 2011 Available at: http://mhmedical.com/ Accessed: May 12, 2017 apoptosis and remodeling. Copyright © 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved