* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Can any cell become a cancer?
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
BRCA mutation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
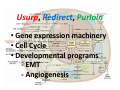
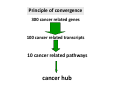
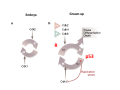
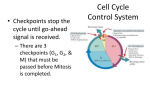
? Can any cell become a cancer? Does this really occur in nature? To build a cancer from scratch, which cell would you start with? Properties a cell must acquire GENESIS to become malignant •Autonomy ‐ Proliferation ‐ Survival ‐ Matrix ‐ Neighbors •Maintain telomeres (hTERT) Properties a cancer must acquire to cause disease •Recruit a circulation •Motility •Invasiveness Usurp, Redirect, Purloin • Gene expression machinery • Cell Cycle • Developmental programs ‐ EMT ‐ Angiogenesis Cancer is a genetic disease • Mutate • Amplify • Delete Cancer is a genetic disease • Gain of oncogenes • Loss of tumor suppressors Usurp, Redirect, Purloin • Gene expression machinery • Cell Cycle • Developmental programs ‐ EMT ‐ Angiogenesis oncogene A gene that normally directs cell growth. If altered by a gain of function mutation, an oncogene can promote or allow the uncontrolled growth of cancer. Alterations can be inherited or caused by an environmental exposure to carcinogens. Inherited cancers caused by oncogenes MEN2 ‐ RET: member of the cadherin superfamily, encodes receptor tyrosine kinases Noonan Syndrome ‐ Shp2 and SOS1: Upstream in the Ras pathway tumor suppressor gene A type of gene that helps control cell growth. A loss of function mutation in a tumor suppressor gene predisposes to cancer. Inherited cancers caused by tumor suppressors LOH ALL OTHERS ONCOGENIC MUTATIONS How to evade defenses? Order of operations? Cancer What are the defenses? • Organism level – Innate immunity – Adaptive immunity – Surgeons • Cell level – Apoptosis – Autophagy – Senescence • Subcellular level – Cell cycle checkpoints – DNA repair – Stress responses • • • • • ER stress Nutrient deficiency UPR Heat shock Hypoxia The Cancer Conundrum Despite genetic diversity, deregulation of known cancer genes cause pathological changes in only a small set of cellular pathways that confer a stereotyped malignant morphology and the ability to form tumors and metastasize (Weinberg chapter 2) But epithelial tumors of the same organ display: • Biological similarity • Genetic diversity How is this possible? Random mutations in key pathways lead to cancer? Principle of convergence 300 cancer related genes 100 cancer related transcripts 10 cancer related pathways Hubs in the cell regulatory network controlling cancer related functions Consequences of convergence Key components of the basic cellular machinery are usurped Key developmental and regenerative programs are usurped Based on first principles: to control a cell, which process would you usurp? How does the cell spend its energy? Membrane integrity and ionic gradients = 30% Everything else………………………………………. = 20% Protein synthesis…….= 50% Growth Factor–Growth Factor Receptor1,2,3…i EGF, IGF, HER‐2, … Signal transducer1,2,3…k Ras, tyrosine kinase, … A critical point of convergence Principle of convergence 300 cancer related genes 100 cancer related transcripts 10 cancer related pathways cancer hub Growth Factor–Growth Factor Receptor1,2,3…i EGF PDGF HER‐2 Gefitinib (Irissa) Imatinib (Gleevec) Trastuzumab (Herceptin) Abnormal growth Applying the principle of convergence 300 cancer/growth related genes Targeted drugs 100 cancer/growth related transcripts 10 cancer/growth related pathways Cancer hub New therapeutics Evading: APOPTOSIS AUTOPHAGY SENESCENCE So you want to be a cancer! • Grow without limits – Autonomous proliferation (Destroy the R point) – Evade apoptosis (Destroy the p53 checkpoint) – Evade replicative senescence (telomerase) – Recruit a circulation • Go wherever I want, whenever I want – Ignore matrix cues – Ignore neighboring cells Press Release: The 2001 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 8 October 2001 The Nobel Assembly at Karolinska Institutet has today decided to award The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for 2001 jointly to Leland H. Hartwell, R. Timothy (Tim) Hunt and Paul M. Nurse for their discoveries of "key regulators of the cell cycle" Grown up Embryo R p53