* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A double circulatory system - School
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
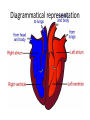
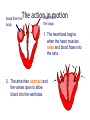
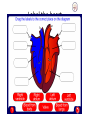
A double circulatory system Because of this our circulatory system is in two parts. It is in fact called a double circulatory system. This section of the system including the right side of the heart, deals with the deoxygenated blood. Lungs Body cells This section of the system including the left side of the heart, deals with the oxygenated blood. One big muscle The heart is made almost entirely of muscle. It is unlike any other muscle in your body because it never tires. And even though it is full of blood it still needs it own blood supply. Oxygenated blood is carried to the heart by the coronary arteries. Each side of the heart has two chambers. 1. An top chamber or atrium and 2. A bottom chamber or ventricle Each of these chambers has its own function. Look at the diagram on the next slide to see what that is. Diagrammatical representation The action in motion Now that we can name all of the parts of the heart it is time to see how they work to push blood around the body. The heart pumps blood when its muscle contracts. As the muscle contracts the chamber gets smaller and squeeze the blood out. The two sides of the heart work together. The atria contract and relax at the same time, as do the ventricles. The next two slides describe what occurs inside the heart during one heart cycle. The actionblood infrom motion blood from the body the lungs 1. The heart beat begins when the heart muscles relax and blood flows into the atria. 2. The atria then contract and the valves open to allow blood into the ventricles. The action in motion 3. The ventricles contract forcing the blood to leave the heart. At the same time, the atria are relaxing and once again filling with blood. The staged cycle then repeats itself. lungs Different destinations This journey is far less demanding. The right ventricle only has to pump blood from the heart to the adjacent lungs. This journey is enormous. The left ventricle has to pump blood all over the body! body cells Therefore, the left ventricle needs a thicker wall to generate a stronger ‘squeeze’ on the blood. Label the heart Answer the questions