* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review of Blood type and Rh
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Plasmodium falciparum wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Atherosclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
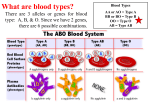
Review of Blood type and Rh Blood types and Blood groups Blood Types- two parts the ABO part and the Rh part. A, B, O specify the types of proteins found on RBC’s. Rh factor is most important factor in Rh disease Rh factor group of proteins that occur only on the surface of RBC’s. Rh factor present on RBC’s then you are Rh positive Rh factor absent on RBC’s then you are Rh neg. Here’s a link that reviews blood typing Rh isoimmunization Rh isoimmunization occurs when an Rh negative mother has an Rh positive child causes the destruction of the infant’s red blood cells (anemia) during pregnancy and after birth Rh disease What happens The immune system recognizes foreign cells (rh positive cells that have transferred from fetus to mother through the placenta) and sets out to destroy the invading cells by forming antibodies to recognize future foreign cells to fight off invasion. Antibodies are produced after the first delivery so first baby is unaffected. Future pregnancies are at risk b/c the body recognizes a fetus with positive blood type as a foreign invasion and the immune response will destroy fetal blood cells. (causing fetal anemia and increase risk for fetal death) Rh isoimmunization Prevention Mother given anti Rh gamma globulin (RhoGAM) at 28 weeks gestation and within 72 hours after delivery, miscarriage, ectopic and for abortions. Prevents the formation of antibodies that might affect future infants. **RhoGAM only affective if mother has not already developed antibodies to rh positive blood type. Care Plan for Hemolytic Disease Severity Zone 1 mild Zone II Upper Zone Zone II III moderate moderate to severe severe Management amnio for delta-OD 450 every 4-5 weeks amnio for delta-OD 450 every 1-2 weeks amnio for delta-OD 450 every 1-2 weeks fetal blood transfusion Delivery 37 weeks 34-36 weeks deliver at if fetal lungs once if fetal lungs are are mature mature at term