* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant and Animal Structure Unit
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
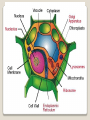
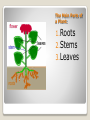
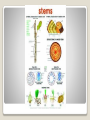
Plant Structure Unit Mrs. Krajewski Plant Characteristics Plant Cells Plants are made a small building blocks called cells. Different parts of a cell do different jobs. Ex: some cells may have the job of making food for the plant CELLS All plants are made up of cells. CELLS: Make up a plant. Cells are organized into tissue and tissue is organized into organs. What do plants need to survive? Plants need: •Sunlight •Water •Carbon dioxide •Minerals from the soil Make a 4 fold! Plant Habitats: Habitats Plants live in many different habitats. Some can survive in extremely cold or hot weather. Some plants such as lilies can grow in water by using the soil at the bottom of a pond! Photosynthesis The process of making the sugar, which is the food the plant needs to survive. Plants make their own food! Let’s read pages 48 and 49! Chorophyll Photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts of leaf cells. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll. “chloro” is a Greek word for “green”. Chlorophyll makes plants green in color. Chlorophyll captures energy from sunlight. Check Point Questions: What are the 3 characteristics of plants? In what part of a plant cell does photosynthesis occur? Questions – Text p. 49 Parts of a Plant The Main Parts of a Plant: 1.Roots 2.Stems 3.Leaves Roots: Grow downward in the soil. a) Function: 1. absorb water from the soil. 2. absorb nutrients from the soil. 3. hold the plant in place Roots 4. roots in some plants store food. 1. 2. 3. Taproots have one lard root (ex: dandelions, carrots, and parsnips). Fibrous Roots spread out and no one root is larger or important than another. Root Hairs: threadlike cells on a root that take in water and minerals. Most roots have root hairs. Types of Roots Tap Roots Fibrous Roots Root Hairs Stems What is a stem? A stem grows above ground level. 1. Carry water , minerals, and nutrients from the roots to the leaves. 2. Support leaves and flower. Stems What is its function? 1. Woody Stems: Are found in larger plants to give the plant extra support. Types of Stems Woody Stems Soft, Green Stems 2. Soft, Green stems: Are found in smaller plants like the strawberry plant or daisies. Types of Stems Woody Stems Soft, Green Stems Leaves What is a leaf? The main foodmaking part of a leaf. 1. 2. 3. 4. Leaves Main Parts: Veins Epidermis Chlorophyll Stomata Veins: are bundles of tubes that carry water to the leaf and food from the leaf to the stem and roots. Chlorophyll: is a green substance which traps the sun’s energy; which is used to make food. Epidermis: is the protective layers that keeps the leaf from drying out and losing water. Stomata: are tiny openings on the bottom side of the leaf, which allows gas and water vapor to pass in and out. Veins, Epidermis, Chlorophyll, and Stomata Leaves Types of Leaves: 1.Pinnate Leaves 2.Palmate Leaves Pinnate: Have parallel veins (running the same direction). Example: grass, corn, tulips, and onions. Pinnate Leaves GRASS LEAVES ONION LEAVES TULIP LEAVES CORN LEAVES Grass, corn, tulips, and onions. Palmate: Have veins that branch out from the center of the leaf. Ex: maple, rose, and poinsettia leaves. Palmate Leaves MAPLE ROSE POINSETTIA Maple, rose, or poinsettia? PINNATE LEAVES PALMATE LEAVES What type of leaf is it? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. PICK A STATE FIND THE STATE FLOWER WRITE ONE FACT ABOUT THE STATE FLOWER DOES IT HAVE PINNATE OR PALMATE LEAVES? PRINT OR DRAW A PICTURE homework Relate to Social Studies Life Cycle of a Flowering Plant Cycle: 1.Seeds 2.Seedlings 3.Mature Plant 4.Flowers 5.Fruit 6.Seed Part 1 Seeds: an underdeveloped plant with stored food sealed in a protective covering, seed coat. Ex: coconut seed Part 2 Seedlings: the germination of a seed sprouting into a new, young plant. Part 3 Mature Plant: the plant has grown enough to produce its own seeds. Part 4 Flowers: the mature plant will produce flowers that will be pollinated by insects or wind. Part 5 Fruit: the ovary of some flowers will grow into fruit which surrounds the new seed. Ex: apples and peaches. Part 6 Seed: the ovary of some flowers become seeds or seed pods. Ex: apples and peaches.