* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Demisemiquavers (32nd Notes)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
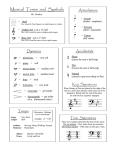
Demisemiquavers (32nd Notes) Demisemiquavers are notes that are worth half of semi quavers or 1/8 of a beat. ½ Beat Quavers (Eighth Notes) Semiquavers (Sixteenth Notes) Demisemiquavers (32nd Notes) + ⅛+⅛ = = ¼ + + ⅛ + ⅛ + ⅛ 1 Tail: Quaver ¼ Beat 2 Tails: Semi Quaver ⅛ Beat 3 Tails: Demi Semi Quaver + = + ⅛ = ½ © A.M Sparrow 2012 Key signatures: Use this chart to tell you how many sharps or flats are in any given key and to work out what the key signature is from any number of sharps or flats. For example, in the Major b's key, Eb has 3 flats in it. Major #’s Minor #’s 0 – Carol 1 – Grows 2 – Daisies 3 – And 4 – Enters 5 – Blooms 6 – F#or 7 – C#ompetition 0 – Animals 1 – Enter 2 – Boats 3 – F#or 4 – C#ruise 5 – G#oing 6 – D#own 7 – A#mazon Major b’s Minor b’s 0 – Chef 1 – Fred 2 – Bbuys 3 – Ebggs 4 – Abnd 5 – Dboes 6 – Gbood 7 – Cbooking 0 – All 1 – Dogs 2 – Give 3 – Cats 4 – Frights 5 – Bbut 6 – Eblephants 7 – Abche © A.M Sparrow 2012 Ledger Lines: Ledger Lines are those lines you may have seen above and below the stave. They are used to indicate notes that appear outside the notes we have on the stave. Middle C is a prime example of this: E B Middle C A You would NOT need the ledger Line above the note of 'B' here B A Do not be afraid of notes on ledger lines as all you need to do is count up or down Them like climbing a ladder. Just count the lines and spaces. Middle C is always easy to recognise and all you need to do to find the note next to Middle C In this example is count backwards through the 'Musical Alphabet' (A-G) counting the lines and spaces. © A.M Sparrow 2012 Transposition: Transposition is where you are moving notes in a piece of music up or down to another pitch. For Grade 3 you will only be: 1) Moving a melody DOWN one octave from the Treble Clef to the Bass Clef. 2) Moving a melody UP one octave from the Bass Clef to the Treble Clef. Middle C 3 4 4 4 Middle C 3 4 4 4 Middle C © A.M Sparrow 2012 Compound Time: Simple Time ( 2 3 or 4 ) beats can be divided by 2. 4 4 4 Compound time beats can be divided by 3. Simple Compound 2 4 6 8 Duple 3 4 9 8 Triple 4 4 12 8 Quadruple Grouping in Compound Time: A general rule of thumb when grouping in compound time is to group in 3's. = NOT Try to think in 3's and when using rests And try to make 3 quaver (eighth) notes © A.M Sparrow 2012