* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gram Staining and Cell Wall Structure
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
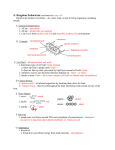
Gram Staining and Cell Wall Structure Most bacteria secrete a covering for themselves which we call a cell wall, However, bacterial cell walls are a totally different thing than the cell walls we talk about plants having. Bacterial cell walls do NOT contain cellulose like plant cell walls do. Bacterial cell walls are made mostly of a chemical called peptidogly (made of polypeptides bonded to modified sugars), but the amount and location of the peptidoglycan are different in the two possible types of cell walls, depending on the species of bacterium. Some antibiotics, like penicillin, inhibit the formation of the chemical cross linkages needed to make peptidoglycan. These antibiotics don't outright kill the bacteria, but just stop them from being able to make more cell wall so they can grow. That's why antibiotics must typically be taken for ten days until the bacteria, unable to grow, die of "old age". If a person stops taking the antibiotic sooner, any living bacteria could start making peptidoglycan, grow, and reproduce. However, because one of the two possible types of bacterial cell walls has more peptidoglycan than the other, antibiotics like penicillin are more effective against bacteria with that type of cell wall and less effective against bacteria with less peptidoglycan in their cell walls. Thus it is important, before beginning antibiotic treatment, to determine with which of the two types of bacteria one is dealing. Dr. Hans Christian Gram, a Danish physician, invented a staining process to tell these two types of bacteria apart, and in his honor, this process is called Gram stain. In this process, the amount of peptidoglycan in the cell walls of the bacteria under study will determine how those bacteria absorb the dyes with which they are stained, thus bacterial cells can be Gram+ or Gram -. Gram+ bacteria have simpler cell walls with lots of peptidoglycan, and stain a dark purple color. Gram- bacteria have more complex cell walls with less peptidoglycan, thus absorb less of the purple dye used and stain a pinkish color instead. Also, Gram- bacteria often incorporate toxic chemicals into their cell walls, thus tend to cause worse reactions in our bodies. Because Gram- bacteria have less peptidoglycan, antibiotics like penicillin are less effective against them. As we have discussed before, taking antibiotics that don't work can be bad for you, thus a good doctor should always have a culture done before prescribing antibiotics to make sure the person is getting something that will help.