* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Tectonics Revolution: how it came about
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
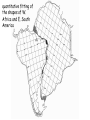
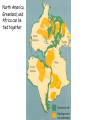
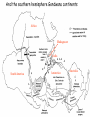
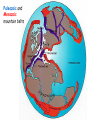
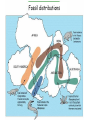
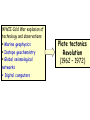
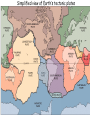
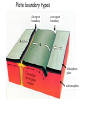
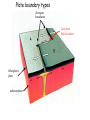
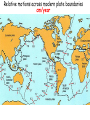
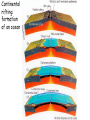
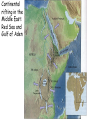
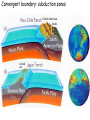
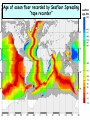
The three pillars of Earth history Stratigraphy Isotope geochemistry Paleomagnetism & plate tectonics The last 200 million years of earth history revealed by paleomagnetism and sea floor spreading* *Link to Quicktime movie Alfred Wegener, a great SES scientist! (1880-1930) - Thermodynamics of the Atmosphere (1911) - The Origin of Continents and Oceans (1915,1929) - Climate and Geological Pre-history (1924) quantitative fitting of the shapes of W. Africa and E. South America The geology matches very closely Proterozoic orogenic belts >2000 Ma cratons North America, Greenland, and Africa can be tied together And the southern hemisphere Gondwana continents Africa Madagascar India South America Antarctica Australia Late Paleozoic Gondwana glaciation Paleozoic and Mesozoic mountain belts Fossil distributions The evidence for continental drift was compelling and well established during the first half of the 20th Century but it was not accepted by many geologists (almost all U.S. geologists) until the advent of plate tectonics in the late 1960’s-early 1970’s! Why?? Why?? Wegener was aggressively attacked and then ignored - because of his lack of geological credentials - his geophysical theories for the dynamics of continental drift were off track Why?? The focus of geologists was on complex continental geology at local to regional scales, not global scales. Why?? The obvious importance of vertical motions in continental geology, leading to the "fixest" (versus "mobilist") synthesis that was the reigning theory for much of the first half of the last century. Why?? the ocean basins were largely “terra incognita” before WWII WWII-Cold War explosion of technology and observations Marine geophysics Isotope geochemistry Global seismological networks Digital computers Plate tectonics Revolution (1962 – 1972) Simplified view of Earth’s tectonic plates Plate boundary types divergent boundary convergent boundary lithospheric plate asthenosphere Plate boundary types divergent boundaries Transform fault boundary lithospheric plate asthenosphere Relative motions across modern plate boundaries cm/year Continental rifting: formation of an ocean Continental rifting in the Middle East: Red Sea and Gulf of Aden Convergent boundary: subduction zones South American Andes island arc The key breakthroughs: • Paleomagnetism • Seafloor Spreading • Contrasting oceanic and continental crustal structure • Seismicity of plate boundaries Plate Tectonics revolution The key breakthroughs: Geomagnetism: major key to Earth’s history • Paleomagnetism • Seafloor Spreading • Contrasting oceanic and continental crustal structure • Seismicity of plate boundaries Plate Tectonics revolution Age of ocean floor recorded by Seafloor Spreading “tape recorder” seafloor age, Ma