* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Parts and Their Functions
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
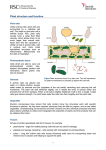
Plant Unit Plant Parts and Their Functions FEATURED SCIENTISTS: Rachel Carson, George Washington Carver Plants have different parts because they live in different environments. For example: Cacti have a thick stem and succulent leaves to store water because they live in dry environments. Mosses have thin stems with small roots because they live an environment with a lot of water nearby. in PLANT PARTS ROOTS have three main jobs: 1. Anchor, or hold, the soil in place 2. Store food 3. Take in minerals and water for the plant There are 3 main types of roots: a. Prop Roots You can find these at the bottom of trees. Seen above ground They keep trees from falling over in wet or loose soil. b. Fibrous Roots You can find these attached to some weeds. They look like tree branches with lots of twigs. They tightly anchor soil which prevents erosion. c. Tap Roots These are found at the base of dandelions. Another example would be carrots. They are single, thick roots that grow straight down into the ground. They store food for the plant. STEMS have two main jobs: 1. Responsible for holding the plant up 2. Carry food (phloem) and water (xylem) to different parts of the plant Stems can be very different. For example, trees have very thick stems (trunks). You can tell the age of a tree by how many rings it has in its trunk. The rings are made from hardened layers of phloem and xylem. This tree was 12 years old because there are 12 rings. 1 Plant Unit LEAVES have two main jobs: 1. The leaves serve as major food factories! Plants make their food during PHOTOSYNTHESIS. Chloroplasts are where chlorophyll is made. The chlorophyll needs sunlight to make sugar. The fall colors of leaves are due to a lack of chlorophyll. 2. Serve as a site for gas exchange: CO2 (carbon dioxide) goes in and H2O and O2 come out. Small holes, called stomata, are on the underside of leaves. They allow these gases to enter and exit. During CELLULAR REPSIRATION plants use oxygen to burn their food to produce energy to grow. Different Kinds of Plants A. Non-vascular Plants Definition: Plants that do NOT have phloem or xylem tubes to carry food, water, and minerals up the stem. These kinds of plants slowly move their food and water from cell to cell. They are tiny and live in very moist areas. They do not have flowers, stems, or seeds. Reproduce with spores. **Spores are single reproductive cells that grow into new plants. Examples: Moss, algae, and liverwort B. Vascular Plants Definition: Plants that DO have phloem and xylem tubes to carry food, water, and minerals up the stem. These kinds of plants can grow larger because the food and water can move faster through the plant. Examples: trees and ferns Two Types of Vascular Plants 1. Gymnosperms Definition: These are plants with unprotected seeds. Example: pine cones Most gymnosperms produce both male and female cones on the same tree. Male cones produce pollen. **Pollen: A yellow, powdery substance that contains the male reproductive cells. Wind pollinates the cones by carrying pollen from the male cone to the female cone. From this, a new seed is formed. 2. Angiosperms Definition: These are plants that have fruit and flowers. Their seeds are protected. For example, the meat of an apple surrounds the seeds in the core. Rain, insects, animals, and people can pollinate these plants. Insects are attracted to the bright colors of the flowers. 2 Plant Unit PHOTOSYNTHESIS How Plants Make Food Photosynthesis: The process by which plants make food by using water, carbon dioxide, chlorophyll, and sunlight. (“photo” means light; “synthesis” means to put together) Only takes place in the leaves Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll. Chlorophyll makes the plant green. During the day, chlorophyll takes in sunlight and changes it to chemical energy. Chemical energy starts a reaction in the chloroplast that splits water into hydrogen and oxygen. CO2 + H2O + sunlight + chlorophyll Glucose and O2 Some of the glucose, or sugar, is used as food for the plant and the rest is stored as starch. The oxygen is released into the air for use by many living things. CELLULAR RESPIRATION Food Energy Cellular Respiration: The process by which plants release stored energy from food to carry on life’s processes. Plants use most of their energy for their life functions such as growth, repair, and reproduction. Takes place when there’s no available sunlight such as night time and cloudy days. O2 and glucose CO2 + water + energy Plants also need extra energy for dry periods. 90% of the energy is used by the plant and the remaining 10% goes to the organism that eats the plant. *Plants can survive in a closed system such as a terrarium because they so both photosynthesis and cellular respiration. As long as there is sunlight, the plant grows and thrives! Photosyntheis Sunlight Carbon dioxide +water Glucose Oxygen Cellular Respiration Glucose +oxygen energy Carbon dioxide water Any other organism such as humans cannot survive in a closed system as they cannot produce their own oxygen and energy! 3 Plant Unit ALL ENERGY COMES FROM THE SUN!!! --------------------------------------------------------------------------CARBON DIOXIDE-OXYGEN CYCLE Plants release oxygen during photosynthesis Animals breathe in oxygen Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Animals breathe out carbon dioxide Plants take in carbon dioxide during photosynthesis POLLUTION: For hundreds of years, the balance between CO2 and O2 stayed even. However, beginning with the Industrial Revolution (nearly 200 years ago), this balance has changed quite a bit. As more and more factories were built, more coal mines were dug and more trees were cut to fuel fires. The amount of CO2 in the air increased while the amount of O2 decreased because trees were being cut faster than they were being replaced. We must remain aware of the level of carbon dioxide in the air…for too much could be poisonous to both plants and animals. What can we do to prevent this from happening? 4