* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Vasculitis
Inflammation wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Behçet's disease wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatoid arthritis wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmunity wikipedia , lookup
Kawasaki disease wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Management of multiple sclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis research wikipedia , lookup
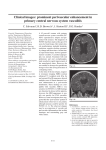
Vasculitis • Vasculitis arises when immune system mistakenly attacks blood vessels. • What causes this attack isn't fully known, but it can result from infection or certain medications. • Severe forms of vasculitis can be caused by the rare autoimmune diseases microscopic polyangiitis and granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Vasculitis • People with these conditions produce harmful antibodies (anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies, or ANCAs) that attack immune cells known as neutrophils. • Resulting inflammation in small- to medium-sized blood vessels can cause severe organ damage and sometimes death. Vasculitis • Diseases characterized by inflammation and necorosis of artery • Primary vasculitis: damage: • Large vessels • Medium vessels • Small vessels • Histological, patogenetic aspects and clinical feature Vasculitis • Cranial arteritis • – prevalence 15-30/100 000 • - incidence 18/100 000 Vasculitis • • • • Polyarteritis nodosa – medium and small vessels Fever, fatigue, loss of weight, artritis, skin changes Myalgia, polyneuropathy Involvement of brain – cca 20% • Wegener granulomatosis – small vessels • Nekrotisans granulomatomas – compression of cranial nerves • Meningitis, hydrocephalus • Polyneuropathy, myelopathy, cerebrovascular diseases • Kidney, lung Vasculitis • Churg-Strauss syndrom • CNS – 6-8% pacients • Stroke – ischemic, hemorrhage, SAH • Behcet disease • Multisystem, chronic-relapsing vasculitis, damage predominantly venous system • Oral ulcerations + genital ulcerations, uveitis, erythema nodosum, • 30% - CNS – lesion of pyramidal tract, stroke, headache, venous sinuses thrombosis Therapy • Combination of immunosuppressive drugs to control the inflammation. • These drugs are commonly high dose steroids (prednisolone) and additional treatment with drugs such as cyclophosphamide or methotrexate may be given. • The amount of steroid treatment will be reduced quickly over the first few weeks and then more slowly. • The current standard of care for ANCA-related vasculitis requires daily doses of the harsh immunosuppressant drug cyclophosphamide for 3 to 6 months. Therapy • Daily doses of another immunosuppressant, azathioprine, then follow for a year or more. • This standard therapy usually clears the vasculitis, but relapse is common. • In addition, this treatment suppresses the immune system in a non-specific way and has potentially severe side effects. • Rituximab is specifically targeted to deplete the type of immune cells thought to produce ANCA. Primary CNS angiitis (PACNS) • Multifocal or diffuse damage of CNS with remittent or progredient clinical course • Leasion of the spinal cord • CSF – increased elements, proteins • AG – narroving and dilatation of the vessels • MRI – ischemic, hemoragic, „tumor-like“ lesions, enhancement of meninges after gadolínium • Brain biopsy Primary CNS angiitis (PACNS) Primary CNS angiitis (PACNS) Primary CNS angiitis (PACNS) • Therapy • Combined immunosuppressive therapy is the treatment of choice for PACNS. • This therapy was initially proposed after its success in patients with systemic vasculitis such as Wegner granulomatosis and polyarteritis nodosa • but is not supported by evidence from controlled trials in PACNS. Primary CNS angiitis (PACNS) • An induction regimen for 9-12 weeks: Cyclophosphamide 2.5 mg/kg/d coupled with intravenous methylprednisolone, 1 g/d for 3 days, then oral prednisolone, 60 mg/d, to be decreased by 10 mg at weekly intervals to reach a dose of 10 mg/d, if possible. • A maintenance regimen for further 10 months: Alternate day steroids (10-20 mg prednisolone) along with azathioprine, 2 mg/kg/d, substituted for cyclophosphamide.