* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ethics in Finance
Investment management wikipedia , lookup
Financial economics wikipedia , lookup
Stock selection criterion wikipedia , lookup
High-frequency trading wikipedia , lookup
Financialization wikipedia , lookup
Short (finance) wikipedia , lookup
Algorithmic trading wikipedia , lookup
Trading room wikipedia , lookup
Amman Stock Exchange wikipedia , lookup
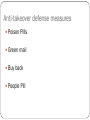
Ethics in Finance by:Karan Srivastava Ethics are standards of right and wrong, good and bad. Ethics are concerned with what one ought to do to fulfill one’s moral duty. There are two aspects to ethics: •Being able to determine what is right or wrong, good or bad •Committing to doing what is right and good Characteristics of Management Prone to Fraud Unduly aggressive financial Targets Domination by person or group without controls Pressure to reduce tax liabilities Non-Financial personnel involved in accounting matters Aggressive accounting practice to keep stock prices high Major performance related compensation Ethical issues in Finance Financial statements Financial Markets Insider Trading Hostile Takeovers Fraud in Financial Statements Fictitious Revenues Concealed Liabilities and Expenses Fraudulent Asset Valuations Improper or Fraudulent Disclosures or Omissions Creative accounting – form of fraudulent financial reporting so as to provide misleading information. Duties of an Auditor To give an accurate statement to the members about the state of affairs of a company To meet the objectives of the Companies Act 1985 and also the Articles of Association To be reasonably skillful and careful in identifying the true nature of the accounts Ethical Audit An audit that assess a business’s structures, procedures, systems and policies. It measures the extent to which the activities of a business comply with the standards it has publicly declared to its external customers It measures business conduct against varied moral standards of the community. Objectives of Ethical Audit To provide a critical assessment of functioning of business To investigate into acquisition or restructuring operations To determine the type of training necessary for employees To establish ethical conduct of business To enhance, measure and promote the quality that increases business performance by assessing them against the ethical business objective To improve the quality of governance by evaluating the performance and ensuring that financial information is both available and reliable Ethical Issues in Financial Markets Deception: act of misrepresenting relevant information Churning: Excessive or inappropriate trading for clients account by a broker who has control over the account with intent to generate commissions rather than to benefit client Unsuitability Unfairness in Markets Introduction Insider trading Insider trading essentially denotes dealing in a company ‘s securities on the basis of confidential information relating to the company which is not published or not known to the public used to make profit or loss. It is fairly a breach of fiduciary duties of officers of a company or “ connected” persons as defined under the SEBI regulations,1992, towards the shareholders. Cont’d Insider terms actually includes both legal and illegal conduct. The legal version is when corporate insider officer, directors , and employees buy and sell stock in their own companies. when corporate insiders trade in their own securities , they must report their trades to SEBI. Illegal insider trading refers generally to buying or selling a security , in breach of fiduciary duty or other relationship of trust and confidence, while in possession of material , non public information about the security. Who are insider traders ????? Remember this ‘STONE COLD’ guy???????? Who are insider traders? Corporate officers, directors , and employees who traded the corporations securities after learning of significant , confidential corporate developments. Friends , business associates, family members , and other types of such officers , directors , and employees, who traded the securities after receiving such information. Cont’d Employees of law, banking , brokerage and printing firms who were given such information to provide services to the corporation whose securities they traded. Govt employees who learned of such information because of their employment by the Govt . Other persons who misappropriated ,and took advantage of, confidential information from their employers. In India……. Only 14 cases taken up by SEBI for insider trading in 2003-04 , which went down to only 7 in 2004-05. In terms of cases completed, the no was only 9 and 5 respectively. So does India has fewer incidence of insider trading or our systems/laws not geared enough to detect such cases? Insider Trading Refers to trading on price sensitive information by company employees or individuals closely connected with the firm This information has not been disclosed to other market participants Ethics & Insider Trading It violates equality of opportunity Does not give a level playing field between insiders and outsiders Might harm exchange as a whole because investors might not be willing to trade on exchange that does not give shareholders their rights. RAJAT GUPTA SCAM HARSHAD MEHTA SCAM Hostile Takeovers Are those that elicit opposition from the boards or employees of Target company Reasons for opposition are as follows: Disagreements over price Protecting their own interests Anti-takeover defense measures Poison Pills Green mail Buy back People Pill Poison Pills An anti-takeover device used by company’s management to make takeover prohibitively expensive for the bidders Company under target changes AOA so that group of Shareholders have special rights to buy and sell preferred stock at highly favorable prices (At times below market price) Greenmail It occurs where a potential takeover agent purchases stock in a company After the purchases have totaled five percent the agent must announce his intention to takeover the company, if that is the intent Stock prices go up in anticipation of takeover battle Management of target company sends greenmails to prevent a shareholder from taking over the company Takeover agent ends up selling the shares back to company at an increased or higher negotiated price Buy Back Purchase of its own shares by the Company Bring down public holding and increases promoter holding A listed Company may buy back its own shares by any of the following methods: Through tender offer; From open market though: Book building process o Stock exchange o People Pill Management threatens that in event of a takeover the entire management team will resign If managers act in their own interest rather than company’s long term value then they are acting unethically