* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ECEN 2612 Two-Port Circuits
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Scattering parameters wikipedia , lookup
Nominal impedance wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
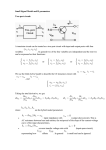
ECEN 2612 Two-Port Circuits (20.0 points) Lab #9 Name: Partner: Objective: Using experimental means, determine values of two-port z parameters and compare with theory. Using OrCAD PSpice, determine a circuit’s two-port parameters. Read through Chapter 18 of the course textbook on Two-Port Circuits to gather an understanding of background information for this lab. Take notes as necessary to aid your lab work. (Refer to instructor supplemental notes online for more details.) Figure 1: Two-Port Circuit Procedure: 1. Set-up and find z parameters. z11 V1 I1 z 22 I 2 0 (5 points) V2 I2 z 21 I1 0 V2 I1 z12 I 2 0 V1 I2 I1 0 (a) Build the two-port circuit shown in Fig. 1 by wiring together the components on the Cadet II breadboard. Make sure to record measured component values using the DMM. After the circuit is built, begin by experimentally determining the four z parameters z11, z12, z21, and z22 as described below. Use the DMM and Agilent DC power supply as necessary. For example, the impedance parameter z11 can be determined by opening port 2 and finding the resistance as seen at port 1. Impedance parameter z22 can be found by opening port 1 and finding the resistance as seen at port 2. To find the transfer impedance z21 assume that port 2 is open, so I2 is 0. Then apply a test voltage across port 1. Measure the current I1 and the voltage V2 while holding the test voltage V1 constant. A test voltage of 10V will work for these measurements. To find the transfer impedance z12 assume that port 1 is open, so I1 equals 0. Then supply a test voltage across port 2. Measure the current I2 and the voltage V1 while holding the test voltage V2 constant. (b) A two-port circuit is reciprocal if the interchange of an ideal voltage source at one port and an ideal ammeter at the other port (while maintaining +/- connections) produces the same ammeter reading. If a two-port circuit is reciprocal then only three calculations or measurements are needed to determine a set of parameters. Determine if the circuit in Fig. 1 is a reciprocal two-port circuit. Provide measurements to support your result. (c) A reciprocal two-port circuit is symmetric if its ports can be interchanged without disturbing the values of the terminal currents and voltages. A symmetric two-port circuit needs only two calculations or measurements to determine a set of parameters. Determine if the circuit in Fig. 1 is a symmetric reciprocal two-port circuit. Provide measurements and descriptions to support your result. (d) Check the experimentally determined values for the four z parameters in part (a) against an analytical solution. Show all work done to compute these values. Be sure to use measured element values, and use KVL/KCL equations as necessary. See text example 18.1 for reference. P.Munro 12-May-2017 10:49 AM Page 1 of 2 2. Analysis of a terminated two-port circuit (4 points) Figure 2: Terminated Two-Port Circuit (a) The two-port circuit shown in Fig. 2 has a “signal generator” (Vg) connected to port 1. Zg might be the internal impedance of the signal generator (use 1k), and ZL is the impedance of a load. Adjust your circuit so that it now represents the circuit in Fig. 2. Measure the input impedance Zin = V1/I1, the load voltage V2, and the output current I2. Discuss the methods chosen to measure each of these three quantities. (b) Compare these measured quantities to the analytical values you obtain using the following sets of theoretical equations and the experimental values of z parameters found in step 1. Use your DMM values. Calculate percent differences as necessary. 3. OrCAD PSpice (5 points) (a) Build the circuit of Fig. 1 in PSpice. Do you need a ground in the circuit? Using PSpice and the methods discussed in part 1 determine the values of the four z parameters z11, z12, z21, and z22. Describe the steps you take to determine each of the different z parameters. Include printouts of the results obtained based on the methods of measurement chosen. (b) Adjust the circuit from part (a) so that it now represents the terminated two-port circuit shown in Fig. 2. Use PSpice to measure the three quantities Zin, V2, and I2. Describe the steps taken to determine Zin, V2, and I2. Include printouts of the results obtained based on the methods of measurement chosen. 4. Tabulation and summary of results (4 points) (a) Discuss and summarize in a table the experimental, theoretical, and PSpice-simulation results for the four z parameters, z11, z12, z21, and z22. (b) Discuss and summarize in a table the experimental, theoretical, and PSpice-simulation results for the input impedance Zin, load voltage V2, and the load current I2 for the terminated two-port circuit in Fig. 2. Normally with PSpice work, at least one example schematic, one or two printed .OUT files, and Probe outputs should be printed and included. Be sure to write notes on your PSpice files to indicate what you see. REPORT: Keep a complete record of all data, results, observations, and answers to questions, written neatly and legibly on the unlined side of standard engineering paper. Attach the lab sheet as a cover. (2 points) This is due at the end of next lab session! P.Munro 12-May-2017 10:49 AM Page 2 of 2