* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Start of the Civil War
Battle of Big Bethel wikipedia , lookup
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Donelson wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
Fort Stanton (Washington, D.C.) wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Union blockade wikipedia , lookup
Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Fort Pulaski wikipedia , lookup
Fort Monroe wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Galvanized Yankees wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Henry wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Hatteras Inlet Batteries wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Port Royal wikipedia , lookup
Jubal Early wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Coast Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
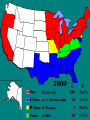
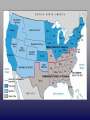
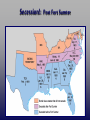
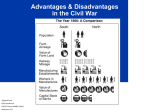
The War Begins 19.1 Presidential election of 1860 In 1860, Stephan Douglas and Abraham Lincoln ran against each other again, this time for president. Lincoln had become well known from their debates about slavery. This time, Lincoln won, becoming the 16th president. Learning Target #1 • Describe what led to the bombardment of Ft. Sumter and explain why this event was important Abraham Lincoln Faced a Crisis • Asked for unity in his inauguration speech Picture Credit: www.branchburg.k12.nj.us/.../ Abe%20Main%20Page.htm Fort Sumter, South Carolina • Since South Carolina had seceded from the United States, it didn’t want Northern soldiers on its land at Fort Sumter • Southern General Beauregard tried to get the northern general Anderson to peacefully l surrender Fort Sumter Fort Sumter: April 12, 1861 • Confederate officials began seizing federalmint branches, arsenals, and military posts. • Fort Sumter was a Federal outpost guarding entrance to Charleston, SC. harbor Fort Sumter: April 12, 1861 • Confederate forces asked for its surrender. • Lincoln refused and sent ships with supplies. • Confederate cannons began firing on April 12, 1861. • Fort Sumter fell 34 hours later. • The Civil War began. Abraham Lincoln • Declared South to be in rebellion • Requested state governors to supply 75,000 militiamen Picture Credit: www.branchburg.k12.nj.us/.../ Abe%20Main%20Page.htm Learning Target #2 • Identify which side of the conflict Arkansas & the Upper South joined & explain why All free Northern states remained loyal to the Union Southern states that had not seceded had to choose sides NC, Tenn, Ark & Va joined Confederacy providing soldiers and industrial resources after Lincoln’s call for troops Four slave states remained in Union Jefferson Davis • President for the South • South’s Capital was Richmond, Virginia http://www.heritagephotographs.com/presjefdav18.html Learning Target #3 •Explain why both North and South wanted to claim the border states The Border States • Ky & Mo controlled key stretches of Ohio & Mississippi Rivers • Maryland enclosed Washington D.C. • People were divided • West Virginia 1863 Which slave states remained in the Union? North South 23 States 11 States Union Confederate Yankee Rebel Blue Coats Grey Coats USA CSA Army of the Potomac River Virginia Federal Northern Advantages • Larger population – North 22 million – South Only 9 million • • • • • More ships Larger, more efficient railroad system Lincoln - Very intelligent and dedicated More industry - 81% of nation’s factories Better banking system to raise $ for the war – 75% of nation’s wealth More Specific Northern Advantages • Wealth produced: – Factory production – Textile goods produced – Iron production – Coal production – Farm acreage – Draft animals – Livestock – Wheat production – Corn production Northern Disadvantages • Fought on Southern lands • Divided support for the war • Many believed the South had good chance of winning Southern Advantages • Skilled officers and a strong military tradition • Other Southern Advantages Fighting a defensive war – Local support of all men – familiarity with terrain • Motivation: seeking independence, unified support • Short communication lines/ friendly population • Experienced officer corps- (Lee, Jackson, Pickett) • Cotton - necessary for textile factories of England and France • Slave Labor in the early part of the war Overview of Southern Disadvantages • Smaller population • Few factories to manufacture weapons and supplies • Poor transportation system • Weak federal government = not strong enough to control Southern states – Jefferson Davis did not have complete power like Lincoln Rating the North & South Learning Target #4 •Analyze the strategies each side followed at the beginning of the war North’s Civil War Strategy: “Anaconda” Plan Goal: surround the Confederacy and squeeze them into submission The Anaconda Plan • Capture Richmond and force surrender • Expel Confederates from border states • Control of the Mississippi River to Stop the transport of: – – – – – – soldiers Weapons Ammunition Clothes Food other supplies needed • Blockade southern ports to stop – cotton shipments – supplies from foreign nations Southern Strategy • Goal: to be recognized as an independent nation in order to preserve their way of life • Defend its homeland, holding onto as much territory as possible until the North got tired of fighting • Capture Washington, D.C. • Control border states • Gain England's support Cotton Diplomacy • Expel Union troops from South Which side was best prepared for victory at the start of the war? Slave/Free States Population, 1861 Railroad Lines, 1860 Resources: North & South Men Present for Duty in the Civil War The Union & Confederacy in 1861 Secession!: Post Fort Sumter