* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Virtual scrring in
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
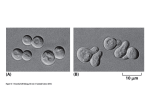
Docking and Virtual Screening Using the BMI cluster Jacek Biesiada Cincinnati, 2008 The Docking Problem Finding the geometry and strength of ligand binding to a receptor. High Throuput Docking and Virtual Screening for Drug Design • Definition of Virtual Screening Use of high-performance computing to analyze large database of chemical compounds in order to indetify possible drug candidates. W.P. Walters, M.T. Stahl and M.A. Murcko, „Virtual Screening-An Overview”, Drug Discovery Today, 3, 160-178 (1998) • Virtual Screening is also known as: • High-Throughput Docking • High-Throughput Virtual Screening Why Use Virtual Screening ? • VS is a computational filter: – Reduces the size of a chemical library to be screened experimentaly ~ 106 to 103 – Saves time & money – ZINC library version 2007, only „drug-like” compounds ~ 2.2 * 106 Expected ZINC version 2008 about 4 * 106 compounds • May improve likelihood of finding interesting compounds – – As oppoesed to random screening Enhance „hit rates” • VS can: – Evaluate virtual combinatorial libraries before synthesized • VS can be usefull tool for discovering new targets in „post-genomic” era Examples of aplications: Design of inhibitors for Norovirus and Glycoprotein IV (collaboration with Jason Jiang, CCHMC and Andrew B. Herr – UC College of Medicine ) Autodock • AutoDock has been widely-used and there are many examples of its successful application in the literature: (First clinicaly-approved HIV Integrase Inhibitor – Autodock used during the research – prof. Andrew McCammon) • Citation Index showed more than 1100 publications have cited the primary AutoDock methods papers. • It is very fast, provides high quality predictions of ligand conformations, and good correlations between predicted inhibition constants and experimental ones. • Very well calibrated force fieled (188 known protein) • Autodock is free software and version 4 is distributed under the GNU General Public License Screening Pipeline: Scripts to Run Autodock on BMI Cluster • Adscr.pl – input: Receptor.cfg adscr.cfg Ligand_info[1-N_CPU] – output: *_ki, *_cl. *_bestlig, *_currentlig, *_errors • Que.pl - input: Number_of_CPU Receptor.cfg Ligand_info_all • Best.pl - input: File with results (*_ki) • Restart.pl – building new Ligand_info_all file in case of restart of calculation Ligand_info_all (Ligand_info) – example: 862418 862450 ZINC00041309 3_p0.0.pdbqt 2 862453 862484 ZINC00041344 3_p0.0.pdbqt 3 862487 862528 ZINC00041448 3_p0.0.pdbqt ...................... 2200000 line ................................ Preparing Receptor and Ligand for Docking Simulations • Prepare_receptor.pl – input: Receptor.pdb 3(4) • Prepare_gpf.pl - – input: Receptor.pdb Ligand.pdb 3(4) binding site, grid box • Autogrid.pl – input: Receptor.pdb Ligand.pdb 3(4) • Configure: Receptor.cfg adscr.cfg - Read the „Tutorial” connected to prepared scripts – all details connected with Virtual Screening Our Library of Compounds • Library in directory • ZINC offer four formats: – sdf, mol2, Smail and flexibase /database/Zinc/ /mol2 /sdf /pdb /pdbq /pdbqt (version from 2007) /sdf_index /pdb_index /pdbq_index (Autodock v.3) /pdbqt_index (Autodock v.4) Virtual Screening is CPU Intensive: Some Estimates Using BMI Cluster • 2.2 mln compounds • On average 1 min for one docking (depends of grid map and several search parameter – with default value) • 50 CPU • ((2200000/50)/ 60min)/ 24h ~ 30 day • About 30 days – 1th screeaning Validation and Analysis of Docking Results • Similarity compounds molprint2d – http://www.molprint.com (free) Method based on MOLecular fingerPRINT • ADME (absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretation) Paramaters like: Molecular weight, LogP, LogD, pKa , number of H-bond donor/acceptor, PSA, ,... (15-16 parameters) ALOGS – http://www.vcclab.org/lab/alogps (free) JChem (MARVIN, JCLUSTOR) – http://www.chemaxon.com/ (free for academic research) Future Work • • • • • Testing scripts Increase library of compounds Writing good „Tutorial” for users Gold standard – similarity and ADME ? Improve scripts for finall-automatic analisys of docking, similarity and ADME. »THANK YOU