* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LN #12 Viruses
Viral phylodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Bacteriophage wikipedia , lookup
Social history of viruses wikipedia , lookup
Virus quantification wikipedia , lookup
Negative-sense single-stranded RNA virus wikipedia , lookup
Oncolytic virus wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to viruses wikipedia , lookup
Plant virus wikipedia , lookup
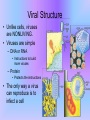
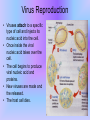
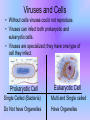
Viruses LN # 13 What is a Virus? • Viruses are a lot smaller than bacteria or animal cells. • Unlike cells that are living, viruses are nonliving. • They are unable to grow and reproduce on their own and therefore must infect cells to do so. Viral Structure • Unlike cells, viruses are NONLIVING. • Viruses are simple – DNA or RNA • Instructions to build more viruses – Protein • Protects the instructions • The only way a virus can reproduce is to infect a cell Virus Reproduction • Viruses attach to a specific type of cell and injects its nucleic acid into the cell. • Once inside the viral nucleic acid takes over the cell. • The cell begins to produce viral nucleic acid and proteins. • New viruses are made and the released. • The host cell dies. Viruses and Cells • Without cells viruses could not reproduce. • Viruses can infect both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. • Viruses are specialized; they have one type of cell they infect. Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell Single Celled (Bacteria) Multi and Single celled Do Not have Organelles Have Organelles Modes of Infection • Virus may live outside of the host, until ready to infect. • Route of infection for cold virus – – – – Nose Eyes Mouth Nasopharynx • Once inside the body, virus will target and infect a cell. How to prevent spread • Wash your hands • Viruses can be on – – – – Phones Money Door handles Anything we touch • Don’t share drinks or food. • Sneeze into your sleeve or tissue – Throw away used tissues Summary 1. 2. 3. 4. What is a virus? What must a virus do in order to reproduce? What are virus made of? Describe the steps for virus replication (2 or more sentences. 5. How are viruses and cells different? 6. What are the modes of infection? 7. How can you prevent the spread of viruses?