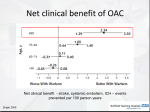
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download N-Acetylneuraminic acid
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
12-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of neuraminidase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
N-Acetylneuraminic acid NHAc Product Code: MA00746 CAS Number: 131-48-6 Chemical Formula: C 11 H 19 NO 9 Molecular Weight: 134.13 Synonyms: O HO OH HO OH CO2H OH Sialic acid Neu5Ac Sialic acid is a commonly used generic term for O- or N-substituted derivatives of the ninecarbon monosaccharide neuraminic acid. N-Acetylneuraminic acid is the most common derivative found in mammalian cells, and sialic acid is often used to refer specifically to this molecule. The abbreviations Neu5Ac or NANA are also used. N-Acetylneuraminic acid is widely distributed in human tissues and is found in glycoproteins on cell membranes and in glycolipids such as gangliosides, and is involved in diverse biological functions including neurotransmission, leukocyte extravasation, viral or bacterial infections and carbohydrate-protein recognition events leading to cell adhesion.1,2 N-Acetylneuraminic acid is also found in several body fluids such as saliva, urine, amniotic fluid and cerebrospinal fluid. As a negatively charged, non-reducing sugar, N-Acetylneuraminic acid is more difficult to analyse directly than reducing sugars such as glucose or lactose. Enzymatic methods for detection in fluids such as serum have been developed, which rely upon the cleavage of pyruvic acid from the molecule by N-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase (also known as N-acetylneuraminate pyruvate lyase), forming N-acetylmannosamine (ManNAc), Scheme 1.3,4 Subsequent oxidation of pyruvic acid to hydrogen peroxide by pyruvate oxidase and colourimetric detection, or reduction of pyruvic acid by lactate dehydrogenase in the presence of NADH and photometric detection form the basis of the quantitative analytical methods. OH HO H HO O O CO2H OH N H N-Acetylneuraminic acid aldolase O HO HO O + NHAc HO OH OH OH O Pyruvic acid ManNAc Scheme 1 Neuraminidase enzymes (sialidases) cleave N-Acetylneuraminic acid and related sialic acids from glycoproteins and glycolipids. Influenza viruses require neuraminidase activity to degrade cellsurface receptors, facilitating release of viral particles from infected cells.5 Neuraminidase inhibitors such as Zanamivir and Oseltamivir (Scheme 2) are effective influenza treatments.6,7 A colourimetric assay for sialidase activity using the Neu5Ac derivative 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolylα-D-N-acetylneuraminic acid 1 (Product code EB02506) has been reported as a test for bacterial vaginosis, a condition associated with endometriosis and pre-term labour.8 Carbosynth Limited 8&9 Old Station Business ParkCarbosynth - ComptonLimited - Berkshire - RG20 6NE - UK 8&9 Old Station Business Park - Compton - Berkshire - RG20 UK 579444 www.carbosynth.com [email protected] Tel: +44 1635 578444 Fax: 6NE +44 -1635 www.carbosynth.com [email protected] Tel: +44 1635 578444 Fax: +44 1635 579444 OH HO H HO O O CO2H O O HN NH2 Zanamivir CO2H Cl O Br O NHAc NH2 NH H HO NHAc NHAc OH HO N H OH Oseltamivir 1 Scheme 2 The utility of N-acetylneuraminic acid in synthetic carbohydrate chemistry has proved challenging, and the development of new methodology for O-sialations is an active field of research.9,10 Ikeda and co-workers have reported the synthesis of phenyl 2-α-selenoglycosides (4) and glycosyl thioimidates (5) of N-acetylneuraminic acid, readily formed in two steps from the methyl ester of Neu5Ac (2), Scheme 3.11,12 Derivatives 4 and 5 are subsequently used as glycosyl donors in glycosylation reactions, as shown in Scheme 4 for the coupling of 5 with protected galactose 6 as the acceptor. OAc OR OR H O OR CO2Me PhSeH, i-Pr2NEt or : OAc X 1,3-benzothiazole-2-thiol i-Pr2NEt, CH2Cl2 NHAc OR AcCl 2, R=H, X=OH OAc H O 4, Y = CO2Me Se Y NHAc 5, Y = OAc N S S 3, R=Ac, X=Cl Scheme 3 AcO O HO + 5 O O AgOTf, CH2Cl2, rt O AcO OAc H O O AcHN O OAc 6 CO2Me O O O O O 54%, a:b = 1:3 Scheme 4 References: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Rahmann, H.; Rosner, H.; Breer, H. J. Theor. Biol. 1976, 57, 231. Szabo, Z. B.; Borbas, A.; Bajza, I.; Liptak, A.; Antus, S. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 1196. Sugahara, K.; Sugimoto, K.; Nomura, O.; Usui, T. Clin. Chim. Acta 1980, 108, 493. Kolisis, F. N. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 1986, 8, 148. Resende, R.; Glover, C.; Watts, A. G. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 4009. Von Itzstein, M.; Wu, W.-Y.; Jin, B. Carbohydr. Res. 1994, 259, 301. Eisenberg, E. J.; Bidgood, A.; Cundy, K. C. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 1949. Wiggins, R.; Crowley, T.; Horner, P. J.; Soothill, P. W.; Millar, M. R.; Corfield, A. P. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 3096. Boons, G.-J.; Demchenko, A. V. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 4539. Kobayashi, S.; Sugiura, M.; Kitagawa, H.; Lam, W. W. L. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 2227. Ikeda, K.; Sugiyama, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Sato, M. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2002, 12, 2309. Ikeda, K.; Aizawa, M.; Sato, K.; Sato, M. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 2618. Carbosynth Limited 8&9 Old Station Business ParkCarbosynth - ComptonLimited - Berkshire - RG20 6NE - UK 8&9 Old Station Business Park - Compton - Berkshire - RG20 UK 579444 www.carbosynth.com [email protected] Tel: +44 1635 578444 Fax: 6NE +44 -1635 www.carbosynth.com [email protected] Tel: +44 1635 578444 Fax: +44 1635 579444