* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Confusing Irregular Verbs
Germanic weak verb wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Germanic strong verb wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Hungarian verbs wikipedia , lookup
Russian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish verbs wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Dutch grammar wikipedia , lookup
Bulgarian verbs wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
English verbs wikipedia , lookup
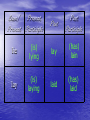
Confusing Irregular Verbs Review •What is a regular verb? •What is an irregular verb? Lie vs. Lay Definitions: LIE= to rest or recline LAY= to place or put Base/ Present Present Participle lie (is) lying lay (is) laying Past Past Participle lay (has) lain laid (has) laid Notice this? The past form of lie and the present form of lay are the same! TIP Typically, lay requires a direct object. Examples 1. I (lie, lay) in bed for a long time on 2. 3. Saturday mornings. My mother (lies, lays) my little sister’s clothes out every morning. (Lie, Lay) the tablecloth out for dinner tonight. TIP Double check sentences without direct objects. If the verb can be replaced by the definition (placed or put), then use lay. Examples 1. The books (lay, laid) on the table. 2. Go (lie, lay) on the couch for a while. 3. The vegetables have been (lay, laid) out on the platter. Sit vs. Set Definitions: SIT= to rest or recline SET= to place or put Base/ Present Present Participle Past Past Participle sit (is) sitting sat (has) sat set (has) set set (is) setting TIP Typically set requires a direct object. Examples: 1. The student (sat, set) in his desk. 2. The teacher (sat, set) the papers on the table. TIP Occasionally, set will not have a direct object. Remember the definition and see if you can replace the verb with placed or put. Examples 1. The books have been (sat, set) on the table. 2. I (sat, set) the cat down on the table. 3. I (sat, set) on the chair. 4. (Sat, Set) the box over there. Rise vs. Raise Definitions: RISE= to go up without help RAISE= to go up with help Base/ Present Present Participle rise (is) rising raise (is) raising Past Past Participle rose (has) risen raised (has) raised Tip • Typically, raise requires a direct object. Examples 1. I (rose, raised) early this morning. 2. The bread (is rising, is raising). 3. We can (rise, raise) the money for charity. Tip Remember the definitions of rise and raise. If the object goes up on its own, then use rise. If the object requires help, then use raise. Check the definitions even if the sentence has no direct object. Examples 1. The sun (rose, raised) this morning. 2. The flag (rose, was raised) early this morning. 3. (Rise, Raise) your hands, please.